Changing the bit depth
Bit depth refers to the number of bits used to represent a sound. You can increase or decrease a file’s bit depth.
Increasing bit depth
Increasing the bit depth does not improve the quality of a file, but it allows subsequent processing to be performed with increased
precision.
1.
Open a file with a small bit depth.
2.
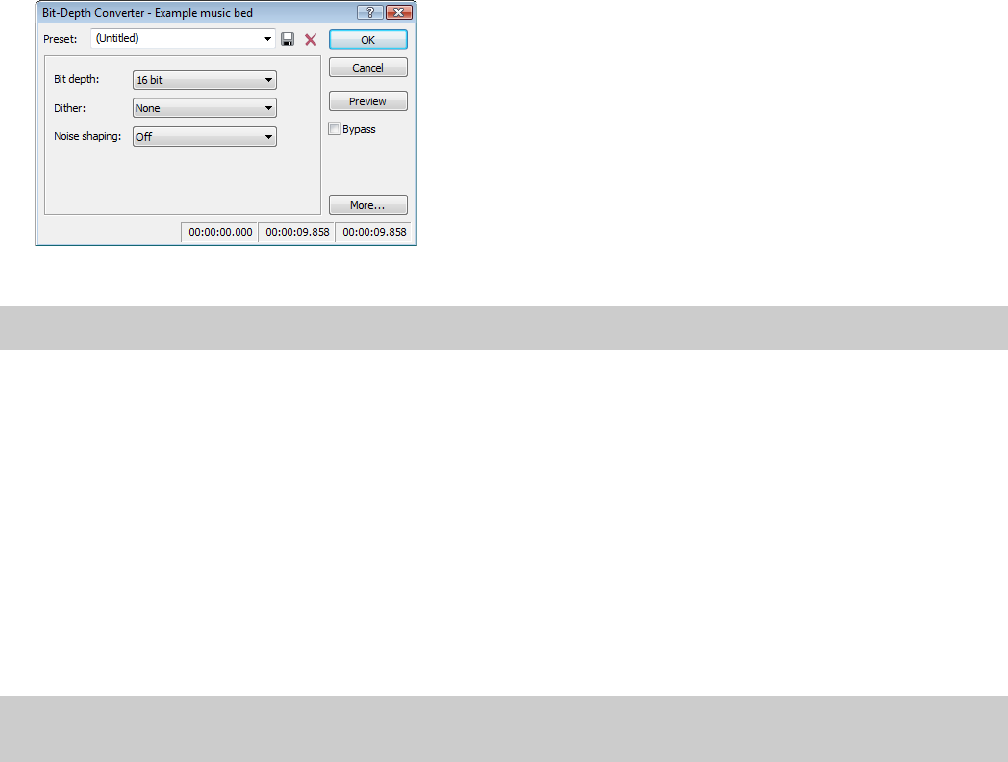
From the Process menu, choose Bit Depth, and then choose Bit-Depth Converter from the submenu. The Bit-Depth Converter
dialog appears.
3.
From the Bit depth drop-down list, choose a larger value and click OK.
Note:
When increasing a file’s bit depth, the Dither and Noise shaping controls should be set to None and Off, respectively.
Decreasing bit depth
To maximize storage space, larger sound files (24- and 16-bit) are frequently converted to smaller (16- and 8-bit) files. However,
representing a sound file at a decreased bit depth results in audible distortion referred to as quantization error.
1.
Open a 16-bit file.
2.
From the Process menu, choose Bit Depth, and then choose Bit-Depth Converter from the submenu. The Bit-Depth Converter
dialog appears.
3.
From the Bit depth drop-down list, choose 8 bit.
4.
If desired, choose an option from the Dither drop-down list. For more information, see Dither on page 103.
5.
If desired, choose a Noise shaping type. For more information, see Noise shaping on page 103.
6.
Click OK.
Note:
There are no rules regarding maintaining audio quality when decreasing bit depth. Experiment with the Dither and Noise
shaping controls to determine the optimum settings for each audio file.
102
| CHAPTER 5
