Appendix C Functional Description C-23
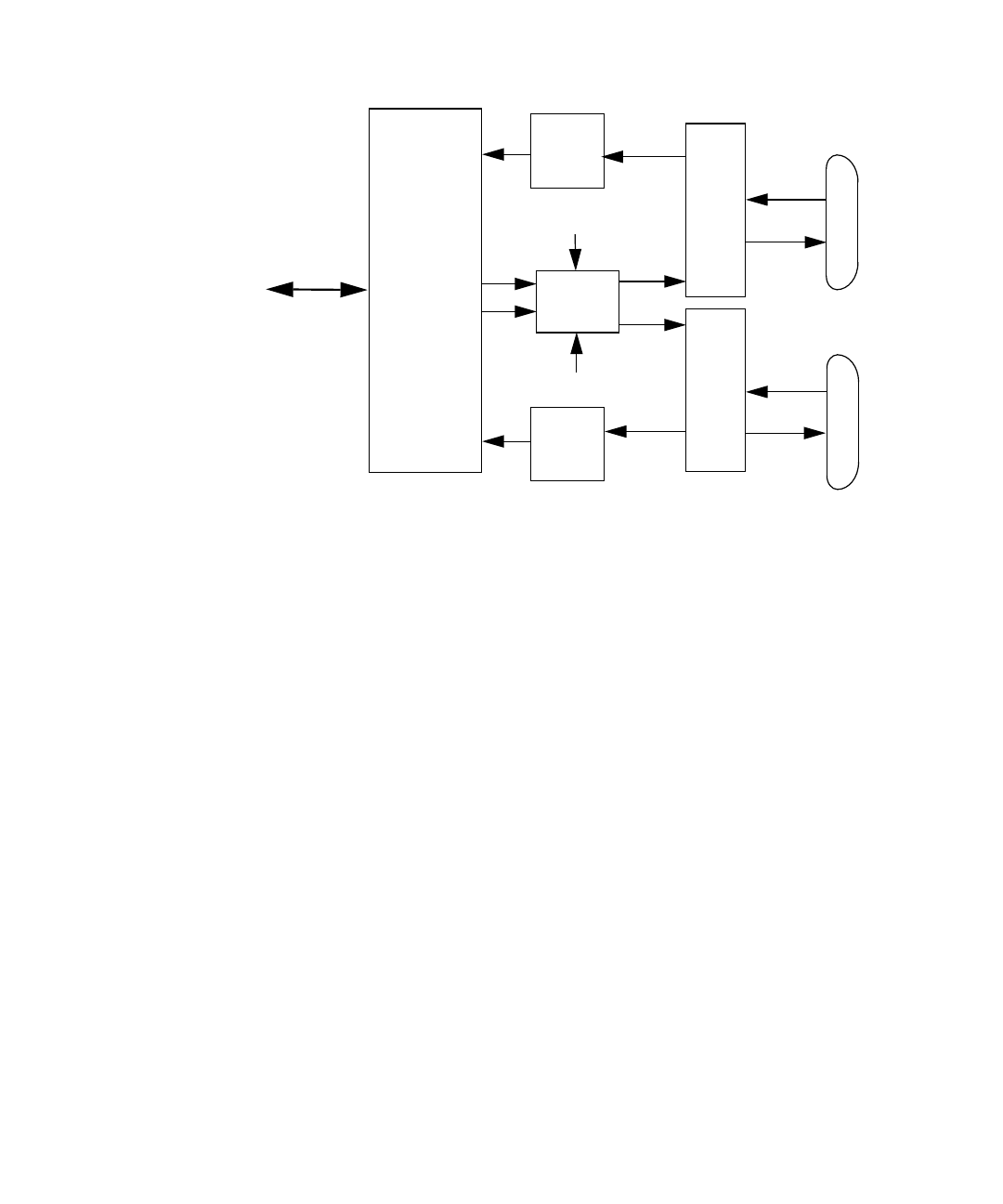
FIGURE C-7 Serial Port Functional Block Diagram
Serial Port Functions
The serial port provides a variety of functions. Modem connection to the serial port
allows access to the internet. Synchronous X.25 modems are used for
telecommunications in Europe. An ASCII text window is accessible through the
serial port on non-graphic systems. Low speed printers, buttonboxes (for
CAD/CAM applications) and exotic devices that function like a mouse are also
accessible through the serial port. The additional speed of the serial port can be used
to execute communications with a CSU/DSU for a partial T1 line to the internet at
384 Kbaud per second.
EIA Levels
Each serial port supports both RS-232 and RS-423 protocols. RS-232 signaling levels
are between -3 Vdc and -15 Vdc and +3 Vdc and +15 Vdc. A binary 1 (001
2
)is
anything greater than +3 Vdc and a binary 0 (000
2
) is anything less than -3 Vdc. The
signal is undefined in the transition area between -3 Vdc and +3 Vdc. The line driver
switches at -10 Vdc and +10 Vdc with a maximum of -12 Vdc and +12 Vdc in RS-232
mode. RS-423 is similar except that signaling levels are between -4 Vdc to -6 Vdc and
+4 Vdc and +6 Vdc. The line driver switches at -5.3 Vdc and +5.3 Vdc with a
maximum of -6 V and +6 Vdc. Switching from RS-232 to RS-423 protocol is
accomplished by changing jumpers J2604 and J2605. Jumper positions 1 and 2 are for
RS-232 and jumper positions 2 and 3 are for RS-423.
Port A
Port B
driver
Line
receiver
Line
Slew rate select
RS-232/-423 select
EBus
Line
receiver
Serial port
controller
EMI
filter
EMI
filter
Serial port A
DB-25
Serial port B
DB-25