25
CHAPTER 3 REGISTER DESCRIPTIONS
3.3.4 Return Pointer (RP)
The return pointer (RP) is a register used to contain the program counter (PC) value
during execution of call instructions, in order to assure return to the correct address
after the call instruction has executed.
■ Overview of the Return Pointer
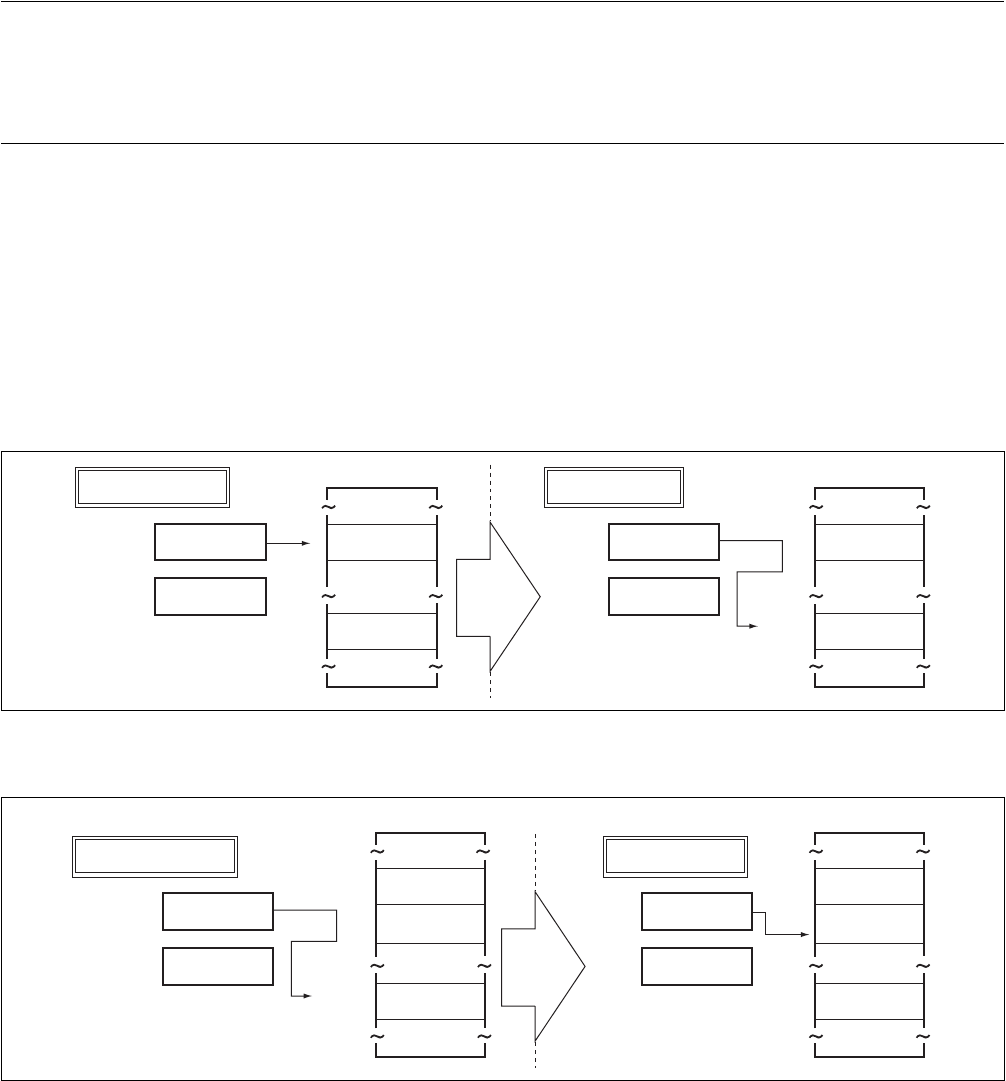
The contents of the return pointer (RP) depend on the type of instruction. For a call instruction with a delay
slot, the value is the address stored +4, and for a call instruction with no delay slot, the value is the address
stored +2. The save data is returned from the "RP" pointer to the "PC" counter by execution of a "RET"
instruction.
Figure 3.3-9 shows a sample operation of the "RP" pointer in the execution of a "CALL" instruction with
no delay slot, and Figure 3.3-10 shows a sample operation of the "RP" pointer in the execution of a "RET"
instruction.
Figure 3.3-9 Sample Operation of "RP" in Execution of a "CALL" Instruction with No Delay Slot
Figure 3.3-10 Sample Operation of "RP" in Execution of a "RET" Instruction
Memory space
CALL SUB1
RET
Before execution
12345678
H
????????
H
PC
RP
Memory space
CALL SUB1
RET
After execution
SUB1
1234567A
H
PC
RP
SUB1SUB1
Memory space
CALL:D SUB
RET
After execution
1234567A
H
1234567A
H
PC
RP
Memory space
CALL SUB1
RET
Before execution
SUB1
1234567A
H
PC
RP
SUB1 SUB1
ADD #1,R00 ADD #1,R00


















