50
CHAPTER 4 RESET AND "EIT" PROCESSING
■ Saving and Restoring Coprocessor Error Information
When a coprocessor is used in a multi-tasking environment, the internal resources of the coprocessor
become part of the system context. Thus whenever context switching occurs, it is necessary to save or
restore the contents of the coprocessor. Problems arise when there are hidden coprocessor errors remaining
from former tasks at the time of context switching.
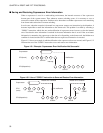
In such cases, when the exception is detected in a coprocessor context save instruction by the dispatcher, it
becomes impossible to return the information to the former task. This problem is avoided by executing a
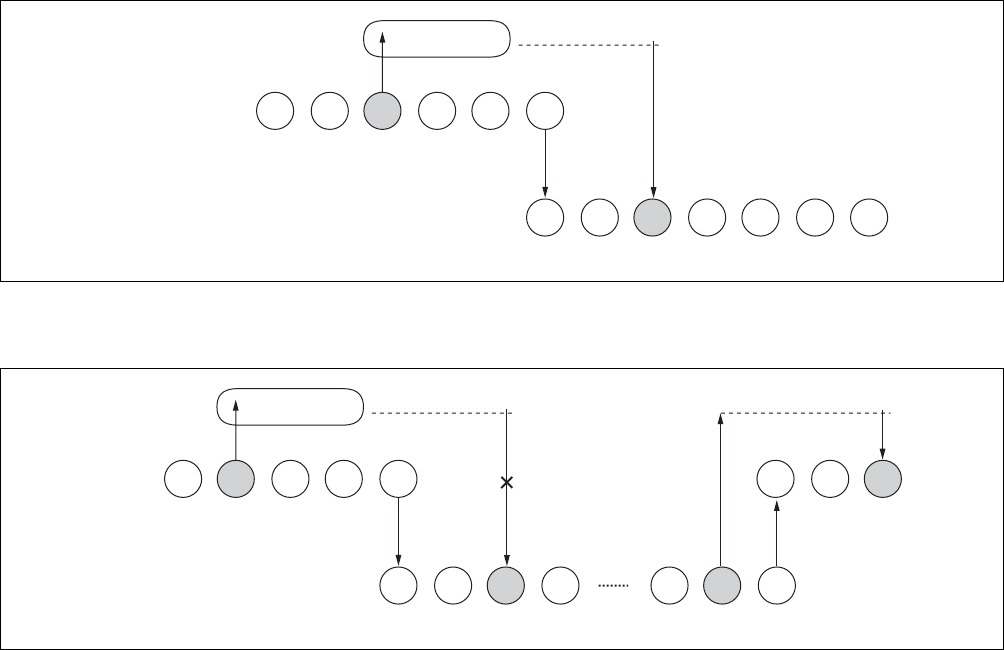
"COPSV" instruction, which does not send notification of coprocessor errors but acts to clear the internal
error. Note that the error information is retained in the status information that is saved. If the saved status
information is returned to the coprocessor at the time of re-dispatching to the former task, the hidden error
condition is cleared and the CPU is notified when the next coprocessor instruction is executed.
Figure 4.5-1 shows an example in which notification to the coprocessor does not succeed, and Figure 4.5-2
illustrates the use of the "COPSV" instruction to save and restore error information.
Figure 4.5-1 Example: Coprocessor Error Notification Not Successful
Figure 4.5-2 Use of "COPSV" Instruction to Save and Restore Error Information
Coprocessor
CPU(main)
CPU(dispatcher)
Hidden error condition
Notification
Interrupt
COPST
COPOP
Coprocessor
CPU
(main)
CPU(dispatcher)
Hidden error condition Hidden error condition
No notification
Interrupt
COPSV COPLD
COPOP
RETI
COPST