CTI 2572 Installation and Operation Guide
139
APPENDIX E. IP ADDRESS INFORMATION
IP Address Nomenclature
Every host interface, or node, on a TCP/IP network is identified by a unique IP address. This
address is used to identify a node on a network and the network to which the node belongs.
Each IP address consists of 32 bits, divided into four 8 bit bytes (called octets). An IP address is
usually expressed in dotted notation, with each octet expressed as its decimal equivalent. See the
example below.
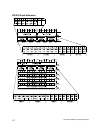
Notation Byte 1 Byte 2 Byte 3 Byte 4
Binary 11000000 11011111 10110001 00000001
Decimal 192 223 177 1
Although an IP address is a single value, it contains two pieces of information: the Network ID and
the Host ID. The Network ID identifies a group of computers and other devices that are all located on
the same logical network. In internetworks (networks formed by a collection of local area
networks), there is a unique network ID for each network. The Host ID identifies a specific device
within a particular network.
The Internet community has defined address classes to accommodate networks of varying sizes. Each
network class can be discerned from the first octet of its IP address. The following table summarizes
the relationship between the first octet of a given address and its Network ID and Host ID fields. It
also identifies the total number of Network IDs and Host IDs for each address class that participates
in the Internet addressing scheme. This sample uses w.x.y.z to designate the bytes of the IP address.
Class w values* Network ID Host ID Number of
networks
Number of
hosts per net
A 1-126 w x.y.z 126 16,777,214
B 128-191 w.x y.z 16,384 65,534
C 192-223 w.x.y z 2,097,151 254
* Inclusive range for the first octet in the IP address. The address 127 is reserved for loopback
testing and inter-process communication on the local computer; it is not a valid network address. W
values above 223 are reserved for Class D - special protocols such as ICMP multicast.
The 2572 will not allow IP addresses which are Class D addresses (254.0.0.0 or greater) or where the
address bits are all zeroes or all ones (0.0.0.0 or 255.255.255.255).