CTI 2572 Installation and Operation Guide
140
Private IP Addresses
If you are planning on connecting to the 2572 modules via the Internet, you must obtain a set of IP
addresses from the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA). You may access the web site at the
following URL: http://www.isi.edu/div7/infra/iana.html. to obtain more information.
If you are certain that you do not need to connect to the Internet, you can use a block of ‘private”
addresses specified in RFC 1597. The private addresses are:
• 10.0.0.0 through 10.255.255.255
• 172.16.0.0 through 172.31.255.255
• 192.168.0.0 through 192.168.255.255
These addresses will not be forwarded by the Internet backbone routers. For more details see the
Web site at http://www.cis.ohio-state.edu/rfc/rfc1597.txt
Subnet Mask
Although the address class concept provides a standard way to determine the network portion of the
IP address there are times that you may wish to further divide an assigned network ID among several
local networks. For example, you may wish to install routers to segment network traffic. The Subnet
Mask provides the means to accomplish this.
The Subnet Mask is a collection of 32 bits that distinguish the network ID portion of the IP address
from the host ID. Subnet masks are determined by assigning 1's to bits that belong to the network ID
and 0's to the bits that belong to the host ID. Once the bits are in place, the 32-bit value is converted
to dotted decimal notation. See the example below.
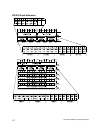
Bits for Subnet Mask Subnet Mask
11111111 00000000 00000000 00000000 255.0.0.0
11111111 11111111 11110000 00000000 255.255.240.0
11111111 11111111 11111111 00000000 255.255.255.0
For example: when the IP address is 128.54.177.97 and the subnet mask is 255.255.255.0, the
Network ID is 128.54.177 and the Host ID is 97.
NOTE:
All computers on a physical network must use the same subnet mask and
network ID; otherwise, addressing and routing problems can occur.
The Subnet Mask must correspond to the address class of the IP Address.
• For a Class A network, at least the first 8 bits must set to 1.
• For a Class B network, at least the first 16 bits must be set to 1.
• For a Class C network, at least the first 24 bits must be set to 1.