Intel® Server Board SE7520JR2 Functional Architecture
Revision 1.0
C78844-002
45
3.3.6.6 Memory Mirroring
The memory mirroring feature is fundamentally a way for hardware to maintain two copies of all
data in the memory subsystem, such that a hardware failure or uncorrectable error is no longer
fatal to the system. When an uncorrectable error is encountered during normal operation,
hardware simply retrieves the “mirror” copy of the corrupted data, and no system failure will
occur unless both primary and mirror copies of the same data are corrupt simultaneously.
Mirroring is supported on dual-channel DIMM populations symmetric both across channels and
within each channel. As a result, on the Server Board SE7520JR2 there are two supported
configurations for memory mirroring:
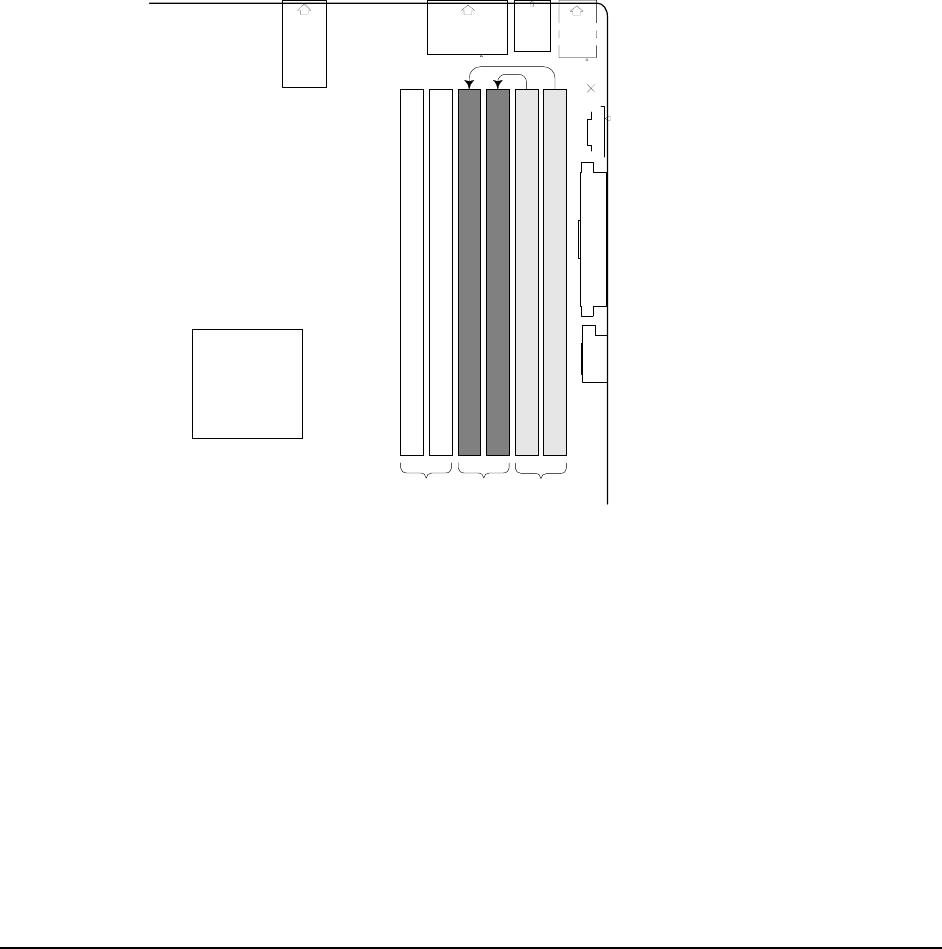
• Four DIMM population of completely identical devices (two per channel). Refer to Figure 6,
DIMMs labeled 1A, 2A, 1B and 2B must all be identical.
Figure 6. Four DIMM Memory Mirror Configuration
•
Six DIMM population with identical devices in slot pairs 1 and 2/3 on each channel. DIMM
slots labeled 1A, 1B must be populated with identical dual ranked DIMMs, while DIMMs in
the remaining slots must be identical single rank DIMMs. DIMMs between the two groups
do not have to be identical. This configuration is only valid with DDR2 memory.
DDR266/333 mirrored memory configurations are only capable of supporting 2 DIMMs per
channel.
D
I
M
M
1
B
MC
D
I
M
M
1
A
D
I
M
M
2
B
D
I
M
M
2
A
D
I
M
M
3
B
D
I
M
M
3
A
Primar
Empt Mirror


















