User’s Manual 295
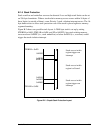
B.1.10 Expanded I/O Memory Addressing
In the Rabbit 3000, only the lower 8 bits of an I/O address were decoded. To provide room
for new peripherals, this was expanded to 16 bits. To ensure backwards compatibility, the
processor always comes up in 8-bit I/O address mode; the 16-bit I/O address mode needs
to be enabled in the MMIDR register by setting bit 7 to 1.
The updated MMIDR register is listed in Table B-20.
NOTE: Bits 7 was always written with a zero in the original Rabbit 3000 chip.
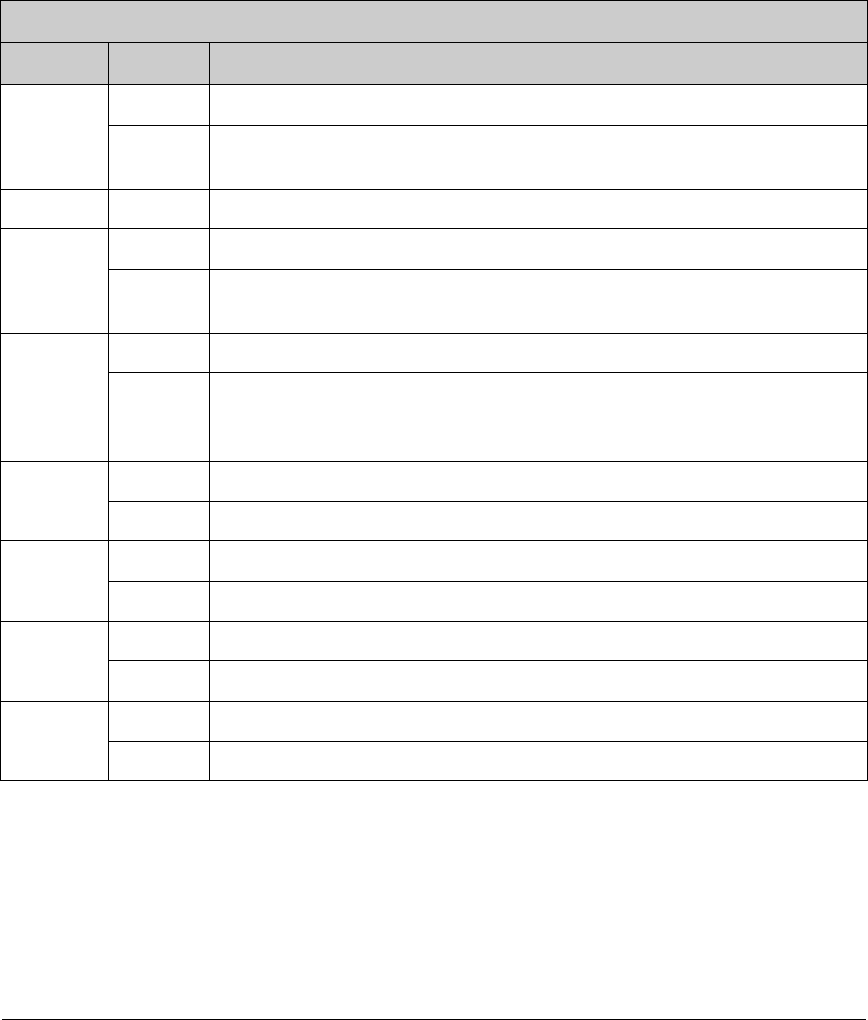
Table B-20. MMU Instruction/Data Register
MMU Instruction/Data Register (MMIDR) (Address = 0x010)
Bit(s) Value Description
7
0 8-bit internal I/O addresses (address range 0x0000–0x00FF).
1
15-bit internal I/O addresses (address range 0x0000–0x7FFF, required to access
internal I/O addresses of 0x0100 and higher).
6 0 This bit is ignored and will always return zero when read.
5
0 Enable A16 and A19 inversion independent of instruction/data.
1
Enable A16 and A19 inversion (controlled by bits 0-3) for data accesses only.
This enables the instruction/data split for the separate I and D space.
4
0 Normal /CS1 operation.
1
Force /CS1 always active. This will not cause any conflicts as long as the
memory using /CS1 does not also share an Output Enable or Write Enable with
another memory.
3
0 Normal operation.
1 For a DATASEG access, invert A19 before MBxCR (bank select) decision.
2
0 Normal operation.
1 For a DATASEG access: invert A16
1
0 Normal operation.
1 For root access, invert A19 before MBxCR (bank select) decision.
0
0 Normal operation.
1 For root access, invert A16