BGP 141
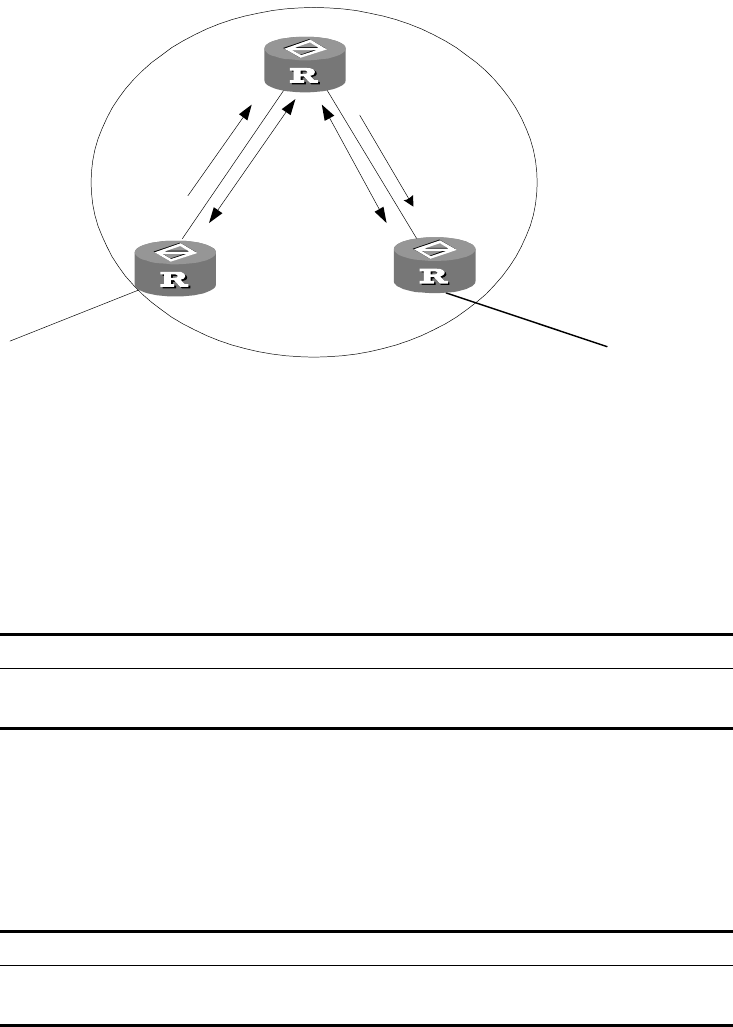
In the following figure, Router A receives an update packet from the external peer
and transmits it to Router C. Router C is a route reflector with two peer clients:
Router A and Router B.
Router C reflects the update packet from client Router A to client Router B. In this
configuration, the peer session between Router A and Router B is actually
eliminated because the route reflector will transfer the BGP information to Router
B.
Figure 12 Route Reflector Diagram
The reflector is the router that can complete the route reflection function. The
route reflector regards the IBGP peers as client and non-client. All peers that do
not belong to this cluster in the autonomous system are the non-clients. The
designation of route reflector and the addition of the client peer are implemented
with the peer reflect-client command.
Configuring the Route Reflection Between Clients
Perform the following configurations in BGP view..
By default, route reflection between clients is enabled.
Configuring the Cluster ID
Generally, there is only one route reflector in a cluster.
Perform the following configurations in BGP view..
By default, the router ID of the route reflector is used as the cluster ID.
Table 123 Configuring the Route Reflection Between Clients
Operation Command
Enable route reflection between clients reflect between-clients
Disable route reflection between clients undo reflect between-clients
Table 124 Configuring the Cluster ID
Operation Command
Configure the Cluster_ID of the route reflector reflector cluster-id { cluster-id | address }
Canceling the Cluster_ID of the route reflector undo reflector cluster-id
Router
EBGP
EBGP
Route reflector
Route reflected
Route updated
Router A
Router B
Router C
Router
EBGP
EBGP
Route reflector
Route reflected
Route updated
Router A
Router B
Router C


















