188 CHAPTER 6: MULTICAST PROTOCOL
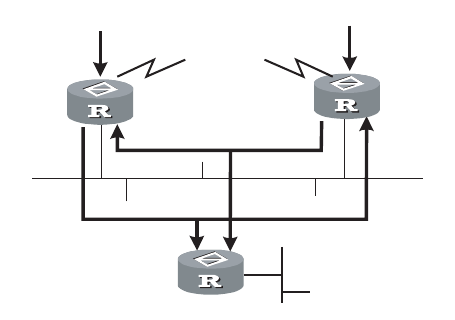
Figure 7 Assert Mechanism Diagram
When they detect such a case, routers need to select a unique sender by using
the assert mechanism. Routers send Assert packets to select the best path. If
two or more have the same priority and metric, the path with a higher IP
address will be the upstream neighbor of the (S, G) entry. This is responsible for
forwarding the (S, G) multicast packet.
■ Graft
When the pruned downstream node needs to be restored to the forwarding
state, the node will send a graft packet to inform the upstream node.
Configuring PIM-DM is described in the following sections:
■ Configuring PIM-DM
■ PIM-DM Configuration Example
Configuring PIM-DM Basic PIM-DM configuration includes:
■ Enabling Multicast
■ Enabling PIM-DM
■ Entering PIM View
Advanced PIM-DM configuration includes:
■ Configuring the Interface Hello Message Interval
■ Configuring the Filtering of Multicast Source/Group
■ Configuring the Filtering of PIM Neighbors
■ Configuring the Maximum Number of PIM Neighbor on an Interface
■ Clearing PIM Neighbors
■ Displaying and Debugging PIM-DM
When the router is run in the PIM-DM domain, it is best to enable PIM-DM on all
interfaces of the non-border router.
Enabling Multicast
See “Configuring Common Multicast ” on page 172.
Multicast packets forwarded
by the upstream node
R
outer A
Router B
Receiver
Router C