218 CHAPTER 7: QOS/ACL OPERATION
IEEE to represent a packet with 802.1Q tag added. The contents of 802.1Q tag
header are shown in
Figure 6.
Figure 6 802.1Q Tag Header
In the figure, the priority field in TCI stands for 802.1p priority, which consists of
three bits. There are eight priority levels, numbered as 0 to 7, for determining
which packets to send first when switch congestion takes place.
Since their applications are defined in detail in the 802.1p Recommendation, they
are named as 802.1p priority levels.
Queue Scheduling
Queue scheduling is used to resolve problems of resource contention by many
packets. The strict priority (SP) and weighted round robin (WRR) algorithms are
often used in queue scheduling.
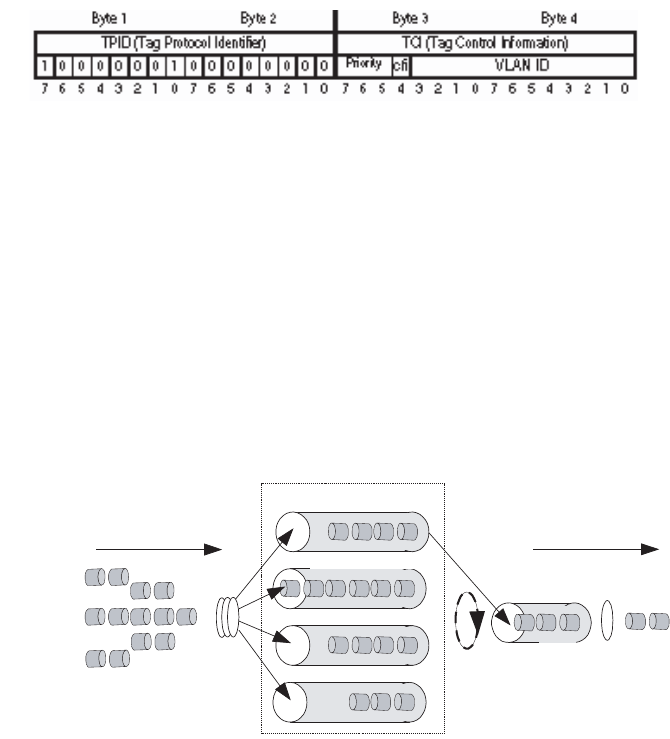
Figure 7 Priority Queues
SP algorithm The SP algorithm is designed for key services. One of the
characteristics of key services is these services should be processed first to
minimize response delay during switch congestion. For example, there are eight
outbound queues at the port, numbered respectively as 7~0, with priority levels in
descending order.
In SP mode, the system first sends those packets of higher priority in strict
accordance with priority order. Only when packets in high priority queue are all
sent can those in lower priority queue be sent. This manner of putting key-service
packets into high priority queue and non-key service packets into low priority
queue does ensure that key-service packets are sent first, while non-key service
packets are sent during the interval when no key-service packets needs to be
processed.
SP algorithm also has its disadvantages: If high priority queues always have
packets for a long period, then the packets in low queues may die of hunger for
being processed.
Packets sent through
this interface
Classify
Packets sent
Sending queue
Dequeue
high queue
middle queue
normal queue
bottom queue


















