Depending on the IS configuration, each IS can run three protocols: ES-IS, IS-IS,
and Connectionless-Mode Network Protocol (CLNP).
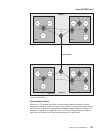
The ES-IS protocol enables the ESs and ISs attached to the same subnetwork to
dynamically discover each other’s existence. An ES connected to the same
subnetwork as an IS is adjacent to the IS. The IS-IS routing protocol enables the
ISs to do the following:
v Dynamically discover the existence and availability of adjacent ISs.
v Exchange routing information with other ISs.
v Use the exchanged routing information to calculate routes based on the shortest
path.
The CLNP protocol is a datagram protocol that transports packets between ISs.
NSAP Addressing
The NPDU contains OSI network addresses (also called NSAPs). The NSAP refers
to a point at the network layer where the user accesses the network layer. NSAPs
are unique points within a system that represent addressable endpoints of
communication through the network layer. The number of NSAPs may vary from
system to system.
An addressing authority, such as the United States government’s National Institute
of Standards and Technology (NIST), administers NSAP addresses and determines
how the addresses are assigned and interpreted within their domain. If desirable,
these authorities may further partition the domain into subdomains and designate
corresponding authorities to administer them.
There are two NSAP addresses within the NPDU, a destination address and a
source address. Each address can vary in length from 2 octets to 20 octets and is
usually represented in hexadecimal notation. The following is an example of a
6-octet NSAP that can be entered in the OSI configuration of the router.
AA000400080C
Because the address length is variable, portions of the PDU header called
Destination Address Length Indicator and Source Address Length Indicator are used
to indicate the length, in octets, of each address.
An NSAP address consists of two parts, an Initial Domain Part (IDP) and a Domain
Specific Part (DSP) as shown in Figure 21.
IDP
The IDP consists of two parts, the Authority and Format Identifier (AFI) and the
Initial Domain Identifier (IDI).
┌───────────┬─────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ IDP │ │
├─────┬─────┤ DSP │
│ AFI │ IDI │ │
└─────┴─────┴─────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
Figure 21. NSAP Address Structure
Using OSI/DECnet V
286
MRS V3.2 Protocol Config Ref Vol 2