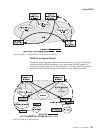
NHRP Auto-Configuration
NHRP is enabled by default if IP is present in the box. It can be disabled by
entering the disable NHRP command from the NHRP config> prompt. See
“Accessing the NHRP Configuration Process” on page 359 for additional
information.
When using an existing configuration file, NHRP is enabled by default if it was not
previously configured. The configuration file will be automatically updated at runtime
to create NHRP shortcut interfaces. You need to save this updated configuration file
and reboot in order for the NHRP client to use LANE shortcuts.
Exclude Lists
Configuration allows you to create a list of protocol addresses (and associated
masks) that represent two types of devices:
v Next-hop routers that do not contain an NHRP server function
v Destination devices to which shortcut VCs should not be allowed
Next-hop Routers:
The exclude list can be used to identify routers that are on the
routed path but do not support NHRP server function.
The server responds to a Next Hop Resolution Request by providing the ATM
address of the next-hop router when all of the following are true:
v The next-hop address is different from the destination address.
v The router interface to the next-hop router is either an ATM classical IP or an
ELAN subnet.
v The next-hop address is in the exclude list.
In processing the request, the router does not forward the Resolution Request on to
the next-hop address, but responds to the client with addressing information that
allows the client to establish a shortcut VC to the next-hop router.
Note: If the next-hop router is one of the Disallowed R2R Shortcuts, the router
sends a NAK to the Resolution Request instead of a positive reply.
In general, if the next-hop router is on the exclude list, the router does not send it
any NHRP packets that would only be handled by an NHRP server.
Destination Devices:
The exclude list can also be used to prevent shortcut VCs
to a given protocol address (for example, a device on a CIP or ELAN subnet that
can support only a small number of VCs).
When processing a Next Hop Resolution Request for a destination device, the
server responds to the client with addressing information that allows the client to
establish a shortcut VC to the router itself when all of the following are true:
v The next-hop address equals the destination address.
v The router interface to the destination is either an ATM classical IP or an ELAN
subnet.
v The destination address is in the exclude list.
Using NHRP
354
MRS V3.2 Protocol Config Ref Vol 2