Chapter 11. Using NHRP
This chapter describes how to use:
v Next Hop Resolution Protocol (NHRP) as specified in Internet Draft Version 13,
which has been submitted for RFC status.
Next Hop Resolution Protocol (NHRP) Overview
The Next Hop Resolution Protocol (NHRP) defines a method for a source station to
determine the Non-Broadcast Multi-Access (NBMA) address of the “next hop”
towards a destination. The NBMA next hop may be the destination itself or the
egress router from the NBMA network that is “nearest” to the destination station.
This “next hop” information is called a “cut-through” route or VC in the NHRP
specification; the router uses the term “shortcut” instead of “cut-through”. The
source station can then establish an NBMA virtual circuit directly with the
destination or the egress router and reduce the number of hops through the
network.
The 2210 can use NHRP to establish shortcuts for IP traffic over the ATM NBMA
network for both RFC 1483 and Emulated LAN (ELAN) interfaces. The Internet draft
does not address the use of NHRP in an ELAN environment, but the 2210 includes
enhancements to allow using LANs. These enhancements are currently
implemented using the vendor-private extensions included in the NHRP protocol
definition.
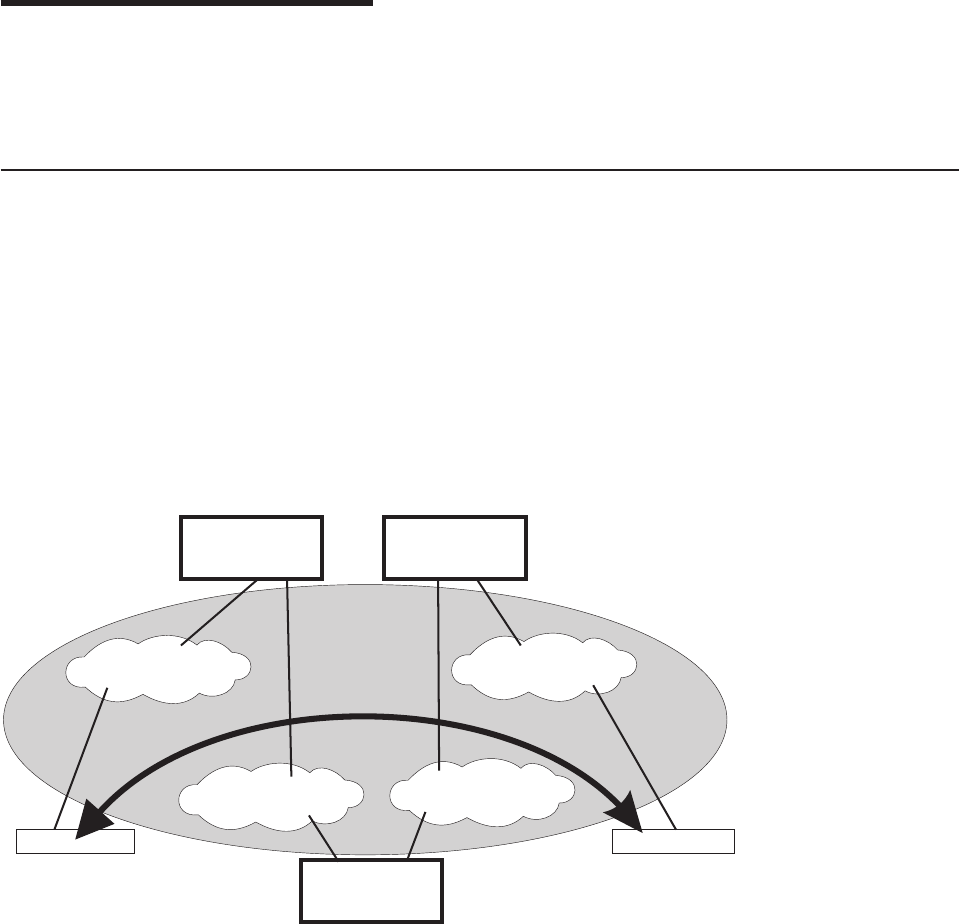
The NHRP draft describes the basic protocol flow as follows: NHRP clients register
their protocol addresses and their NBMA addresses with one or more NHRP
servers. The servers are typically routers on the routed path through the NBMA
network to the clients. When a client wants to establish a shortcut to a destination,
it sends a Next Hop Resolution Request packet along the routed path. The request
NHRP Client
Shortcut VC for client-to-client traffic
NHRP Client
subnet D
ATM
NHRP Server
Router
NHRP Server
Router
NHRP Server
Router
subnet B
subnet A
subnet C
Figure 27. Next Hop Resolution Protocol (NHRP) Overview
© Copyright IBM Corp. 1994, 1998 345