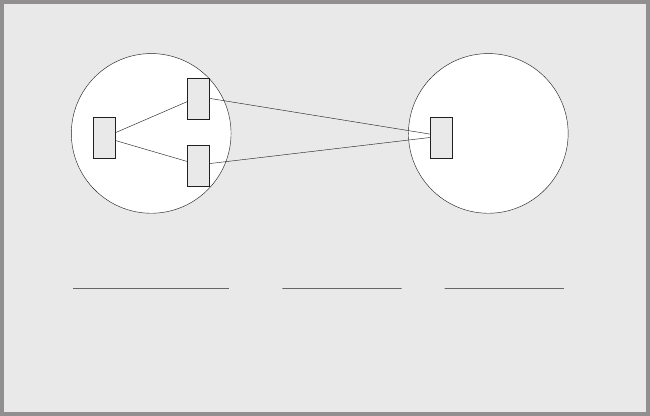
For example, a packet is destined to go from node A in domain 1 to node D in
domain 2 ( Figure 26). Node A can choose two paths to send the packet, to node B
and then on to D or to node C and then on to D. How nodes B and C advertise the
cost of their routes to D determines how node A decides to route the packet,
internally or externally. There are three possible options:
v Nodes B and C advertise the cost of their routes to D as internal. The internal
cost of the route A-B-D is 35 which is the cost of routing from A to B, plus the
cost of routing from B to D. The internal cost of the route A-C-D is 40, which is
the cost of routing from A to C, plus the cost of routing form C to D. Node A in
this case would choose to route over the A-B-D path because the cost is lower.
v Nodes B and C advertise the cost of their routes as external. The external cost
for A-B-D is 30 which is the cost of routing from B to D. The external cost for
A-C-D is 20. Node A in this case would choose to route over the A-C-D path
because the cost of this route is lower.
v Nodes B and C advertise the cost of their routes as both internal and external.
The internal and external cost of the routes are added to their respective routing
tables. Because internal routes are preferred over external routes, the router
chooses the internal route of A-B-D.
Note: Because there is no exterior routing protocol, all prefix routes between
domains must be statically configured.
Address Prefix Encoding
When entering address prefix routes into the router, carefully consider the difference
between encoding rules for NSAPs and for prefix routes. The following four
examples illustrate address prefix encoding.
Encoding a Fixed Length IDI
For many address prefixes, encoding the prefix and the corresponding NSAP is the
same. For example, you are using a GOSIP 1.0 address and you want to create a
route to an organization in the DoD. The Org IDI is 1234 and the DoD IDI is 0006.
The encoded NSAP address is
DOMAIN 1
Routing from A to D
A to B to D
A to C to D
Internal Metric
35
40
External Metric
30
20
DOMAIN 2
30
20
5
20
A
B
C
D
Figure 26. Internal and External Routing Metrics
Using OSI/DECnet V
Chapter 9. Using OSI/DECnet V 297