CDM-Qx Satellite Modem Revision 5
Forward Error Correction Options MN/CDMQx.IOM
6–7
Table 6-4. Available TPC Modes
Code Rate/Modulation Data Rate Range
Rate 21/44 BPSK 32 kbps to 4.772 Mbps
Rate 5/16 BPSK 32 kbps to 3.125 Mbps
Rate 21/44 QPSK 32 kbps to 10 Mbps
Rate 3/4 QPSK 32 kbps to 15 Mbps
Rate 3/4 8-PSK 288 kbps to 20 Mbps
Rate 3/4 16-QAM 384 kbps to 20 Mbps
Rate 7/8 QPSK 32 kbps to 17.5 Mbps
Rate 7/8 8-PSK 336 kbps to 20 Mbps
Rate 7/8 16-QAM 448 kbps to 20 Mbps
Rate 17/18 QPSK 32 kbps to 18.88 Mbps
Rate 17/18 8-PSK 362.7 kbps to 20 Mbps
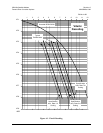
6.5.3 End-to-End Processing Delay
In many cases, FEC methods that provide increased coding gain do so at the expense of
increased processing delay. However, with TPC, this increase in delay is very modest.
The table below shows, for the Modem, the processing delays for the major FEC types,
including the three TPC modes:
Table 6-5. Turbo Product Coding processing delay comparison
FEC Mode (64 kbps data rate) End-to-end delay, ms
Viterbi, Rate 1/2 12
Viterbi Rate 1/2 + Reed-Solomon 266
Turbo Product Coding, Rate 3/4
47
Turbo Product Coding, Rate 21/44, BPSK
64
Turbo Product Coding, Rate 5/16, BPSK
48
Turbo Product Coding, Rate 7/8
245 *
Turbo Product Coding, Rate 17/18
69
Note that in all cases, the delay is inversely proportional to data rate, so for 128 kbps, the
delay values would be half of those shown above. It can be seen that the concatenated
Reed-Solomon cases increase the delay significantly (due mainly to interleaving/de-
interleaving), while the TPC cases yield delays, which are much less.
* A larger block is used for the Rate 7/8 code, which increases decoding delay.