3–1
Chapter 3. FUNCTIONAL
DESCRIPTION
The modem has two fundamentally different types of interface: IF and Data.
• The Data interface can be a bi-directional path, which connects with the
customer’s equipment (assumed to be the DTE) and the modem (assumed to be
the DCE).
• The IF interface provides a bi-directional link with the satellite via the uplink and
downlink equipment.
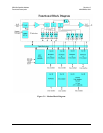
Transmit data is received by the terrestrial interface where line receivers convert the
clock and data signals to CMOS levels for further processing. A small FIFO follows the
terrestrial interface to facilitate the various clocking and framing options. If framing is
enabled, the transmit clock and data output from the FIFO pass through the framer, where
the overhead EDMAC data is added to the main data. Otherwise, the clock and data are
passed directly to the Forward Error Correction encoder. In the FEC encoder, the data is
scrambled, differentially encoded, and then convolutionally encoded. Following the
encoder, the data is fed to the transmit digital filters, which perform spectral shaping on
the data signals. The resultant I and Q signals are then fed to the BPSK/QPSK/
8-PSK/16-QAM modulator. The carrier is generated by a frequency synthesizer, and the
I and Q signals directly modulate this carrier to produce an IF output signal.