CHAPTER 10 Error Notification and Maintenance (Contents, Methods, and Procedures)
10.4 Collecting Maintenance Data
191
C122-E175-01EN
- The responsiveness of the mouse or keyboard is too slow.
Performance deteriorates during system operation when the responsiveness of the mouse or keyboard is
too slow.
For details on memory dump file settings, see 10.4.3 Setting up the dump environment (Windows).
To acquire memory dump, select [Partition] and then the [Power Control] window of the MMB Web-UI.
Specify [NMI] for the target partition.
Remarks
- Forced acquisition of a memory dump causes the server to stop.
- Collection of a memory dump may take a long time depending on the environment.
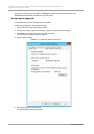
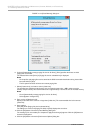
10.4.3 Setting up the dump environment (Windows)
Memory dump is a standard operating system function in Windows. However, before you can acquire dumps,
you need to allocate an area for them on the disk.
This section describes how to set up the environment to acquire memory dumps in Windows. To ensure
system recovery from a failure, configure the following to set up the memory dump environment before
starting to use memory dumps:
Memory dump files and paging files
Memory dump and paging files are described below.
A memory dump file stores debug information on a STOP error (fatal system error) that occurred in the
system.
After installing the operating system and applications for operations, make settings for acquiring memory
dumps.
Different information collected by a memory dump
The PRIMEQUEST 2000 series enables you to acquire the following four types of memory dump. Each type
of memory dump gathers different information.
- Complete memory dump
A complete memory dump records all the physical memory contents at the time when the system stops. It
requires free space equivalent to the physical memory size plus about 300 MB on the boot volume. The
system can store only one dump at a time. The new file would overwrite any existing dump file at the
specified storage location.
- Kernel memory dump
A kernel memory dump records the contents of the Kernel memory space only. For 32 bit windows, dump
file of up to 2GB is created. For 64 bit windows, dump file of up to 8TB is created. The size varies
depending on the situation. The system can store only one dump at a time. The new file will overwrite an
existing dump file at the specified storage location.
- Minimum memory dump
A minimum memory dump records the minimum required data to identify the problem. It requires 128 or
256KB of free space. With this option, the dump function creates a new file each time the system stops
unexpectedly.
- Automatic memory dump
This type of dump is available beginning with Windows Server 2012. "Automatic memory dump" is the
default setting in Windows Server 2012. An automatic memory dump records the same information as a
kernel memory dump. It differs from a kernel memory dump as follows.
- The default setting of the paging file size is a smaller value.
- If all kernel space information could not be recorded, the paging file size is automatically expanded at
the next start time. However, if all kernel space information could not be recorded, memory dump
acquisition may fail.
TABLE 10.7 Memory dump types and sizes
Memory dump type
Memory dump file size
Complete memory dump
Physical memory size + 300 MB (*1)
Overwrite (*2)
Kernel memory dump
Depends on memory space during system
operation (32bit windows:max 2 GB, 64bit
windows max 8 TB).
Overwrite (*2)