Chapter 5: Configuring the Spanning Tree
160
Comparing IP Tunnels to Mobile IP
The AT-WA7500 and AT-WA7501 access points support IP tunneling,
which allows end devices to roam across different subnets (routers)
without having to change IP addresses. IP tunneling supports IETF RFC
1701 using GRE and the same encapsulation technique as mobile IP. IP
tunnels technology is designed primarily to operate in local environments,
where handheld or vehicle-mounted devices may move rapidly between
access point coverage areas on a subnet (although it is possible to attach
a geographically remote subnet through an IP tunnel).
The Internet Engineering Task Force developed RFC 2002, IP Mobility
Support, commonly referred to as mobile IP, to provide mobility for IP
hosts. Mobile IP is designed primarily to address the needs of wireless
end devices that may move between geographically separated locations.
The two technologies are complimentary and may coexist. Both protocols
use similar encapsulation to forward frames to or from end devices that
have roamed away from a root IP subnet. The root access point functions
much like a mobile IP home agent; an access point attached to the remote
end of an IP tunnel functions much like a mobile IP foreign agent.
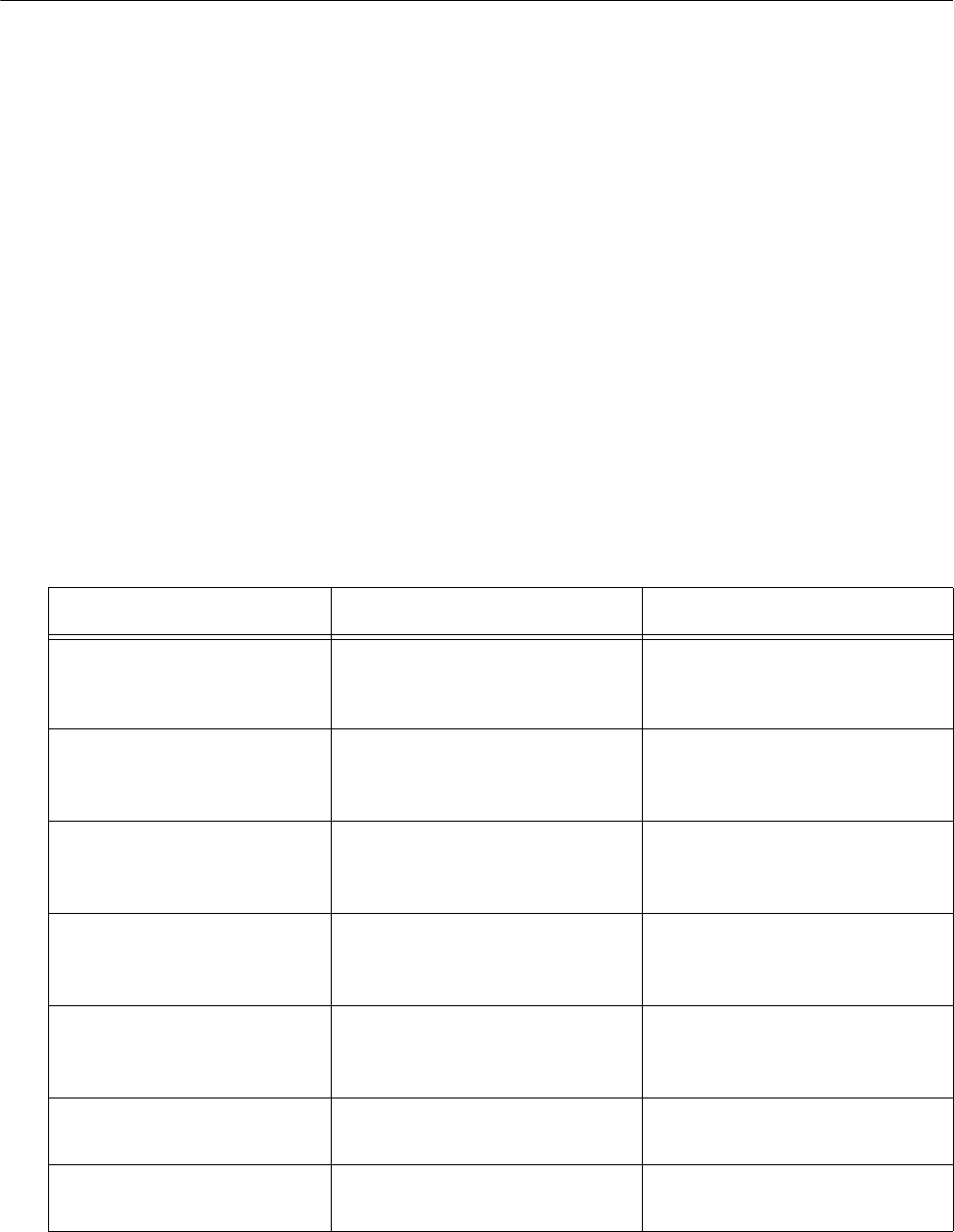
Table 46. IP Tunnels and Mobile IP Comparison
Issue IP Tunneling Mobile IP
Software compatibility No changes are required to
existing IP software stacks in
end devices.
Requires a mobile IP client
software stack in end devices.
Addressing limitations for
IP end devices
Requires that end device IP
addresses belong to the root
IP subnet.
None.
Security Guest addresses are not
used. Data link security.
Mobile IP authentication is
required for “guest” access to
foreign subnets.
Roaming detection Data link indications facilitate
fast roaming with no added
broadcast traffic.
Foreign agent
advertisements.
Roaming restrictions Currently, roaming is limited to
a single network that may
include multiple IP subnets.
None.
Roaming support for non-
IP protocols
Configurable using IP filters. None.
Scalability No practical limitations using
IGMP.
Has no inherent limitations.


















