Chapter 1: Getting Started
26
Figure 10. Access Point as a WAP
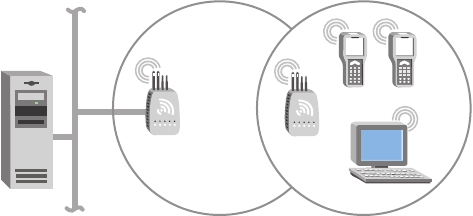
WAPs send data from end devices to the access points via wireless hops.
Wireless hops are formed when data from end devices move from one
access point to another access point through the radio ports. The master
radio in the access point transmits hello messages, which allow the WAPs
to attach to the spanning tree in the same way as access points.
The number of radios required in the WAP depends on the type of radio
installed:
If you have an 802.11a radio, the WAP only needs one radio because
this radio can simultaneously be a master and a station. This radio will
create wireless hops automatically when it cannot communicate to the
wired network.
If you have an 802.11g or 802.11b radio, the WAP must contain two
radios: one configured as master and one as station. The WAP master
radio must match the end devices radios, and the WAP station radio
must match the master radio in the access point.
WAPs must be on the same IP subnet as the access point. Also, data from
wireless end devices should not go through more than three wireless hops
before it gets to an access point on the primary LAN.
The following procedure explains how to install a simple wireless network
with a WAP and no roaming end devices. For help installing a simple
wireless network with a WAP and roaming end devices, see the two
examples in the next sections.
To install a simple wireless network with a WAP and no roaming end
devices
1. Follow the instructions for installing a simple wireless network in the
section “Using One Access Point in a Simple Wireless Network” on
page 21.
2. Configure the LAN ID. For help, see “Configuring the Spanning Tree
Parameters” on page 136.
Ethernet
Access
point
Host
WAP