Chapter 9: Additional Access Point Features
282
Example: The following command takes file AP824X.PRG that is saved in
the active boot drive on the access point client and stores it in the flash
memory segment on the access point server that has IP address 1.2.3.4.
TFTP PUT 1.2.3.4 IB:AP824X.PRG 1:AP824X.PRG
The access point may generate these error messages when it issues a
TFTP PUT command. Other error messages may be returned from the
server and displayed by the access point. See your server documentation
for additional information.
TFTP SERVER LOG
Purpose: The access point can function as a TFTP server. You can use
the TFTP server log command to save a history of TFTP client requests.
The TFTP server log contains useful TFTP server status information. The
log begins when you set up the server. To clear the log, reboot the access
point.
Syntax: TFTP SERVER LOG
TFTP SERVER START
Purpose: Use this command to enable the access point to act as a server.
You can enable one access point to act as a TFTP server and download
files to additional access points.
Syntax: TFTP SERVER START access
where access is blank for read-only access (default), or rw for read/write
access. TFTP does not require any authentication, so a read/write TFTP
server is very insecure and should be used only briefly. When the access
point boots, read-only access is restored.
After you issue this command, the access point responds to TFTP client
requests that are directed to its IP address. When acting as a server, the
access point supports up to four concurrent TFTP sessions.
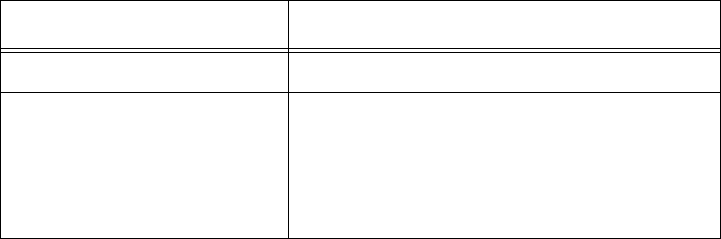
Table 78.
Error Message Explanation
Can’t read file The requested file may not exist.
Invalid opcode during put This error should not occur under normal
operating conditions. This error indicates
a TFTP protocol error that will not occur
when you use TFTP servers that conform
to the protocol.


















