AT-WA7500 and AT-WA7501 Installation and User’s Guide
89
Example 1
This example shows you how to use Ethernet filters to filter all traffic that
passes through the access point to the wireless network except for traffic
for specified MAC addresses. These filters do not prevent wireless traffic
from reaching the Ethernet network. For this example, set these filter
values.
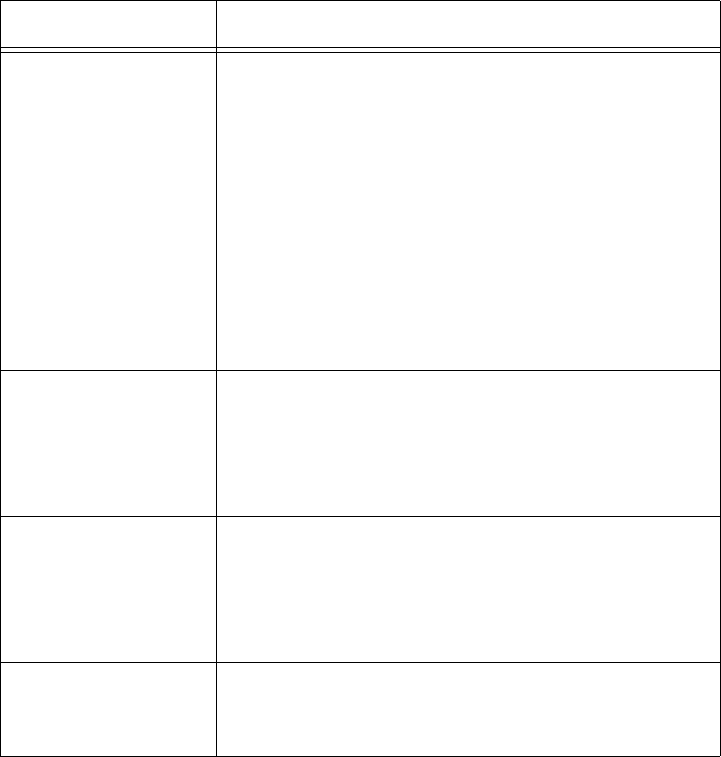
Mask Applies a data pattern to the frame. If the data
pattern in the mask matches the frame, then the
specific action is performed. The mask indicates
the bits that are significant at the specified offset.
A bit is significant if a bit in the mask is set to one.
If this field is empty, the length of the field is
determined by the longest value in the Filter
Values menu for the specified value ID.
The mask values are entered in 0 to 8
hexadecimal pairs.
Op (Operation) Performs a logical operation when a data pattern
matches a value in the Filter Values menu to
determine if the specified action should be taken.
Valid operations include: EQ (equal), NE (not
equal), GT (greater than), LT (less than or equal)
Value ID Represents a value in the Filter Values menu.
The bytes after the frame offset are compared to
the data pattern indicated by the value. Value ID
can be from 0 to 255 and must match one or
more value IDs in the Filter Values menu.
Action Sets the action to Pass, Drop, or And. If you set
the action to And, the filter expression with the
next highest sequence is applied.
Table 21. Filter Expressions Parameter Descriptions (Continued)
Parameter Explanation


















