Advanced Configuration and Management Guide
8. Select the Save
link at the bottom of the dialog. Select Yes when prompted to save the configuration change
to the startup-config file on the device’s flash memory.
PIM Sparse Overview
Software release 06.6.X adds support for Protocol Independent Multicast (PIM) Sparse version 2. PIM Sparse
provides multicasting that is especially suitable for widely distributed multicast environments. The HP
implementation is based on RFC 2362.
In a PIM Sparse network, a PIM Sparse router that is connected to a host that wants to receive information for a
multicast group must explicitly send a join request on behalf of the receiver (host).
PIM Sparse routers are organized into domains. A PIM Sparse domain is a contiguous set of routers that all
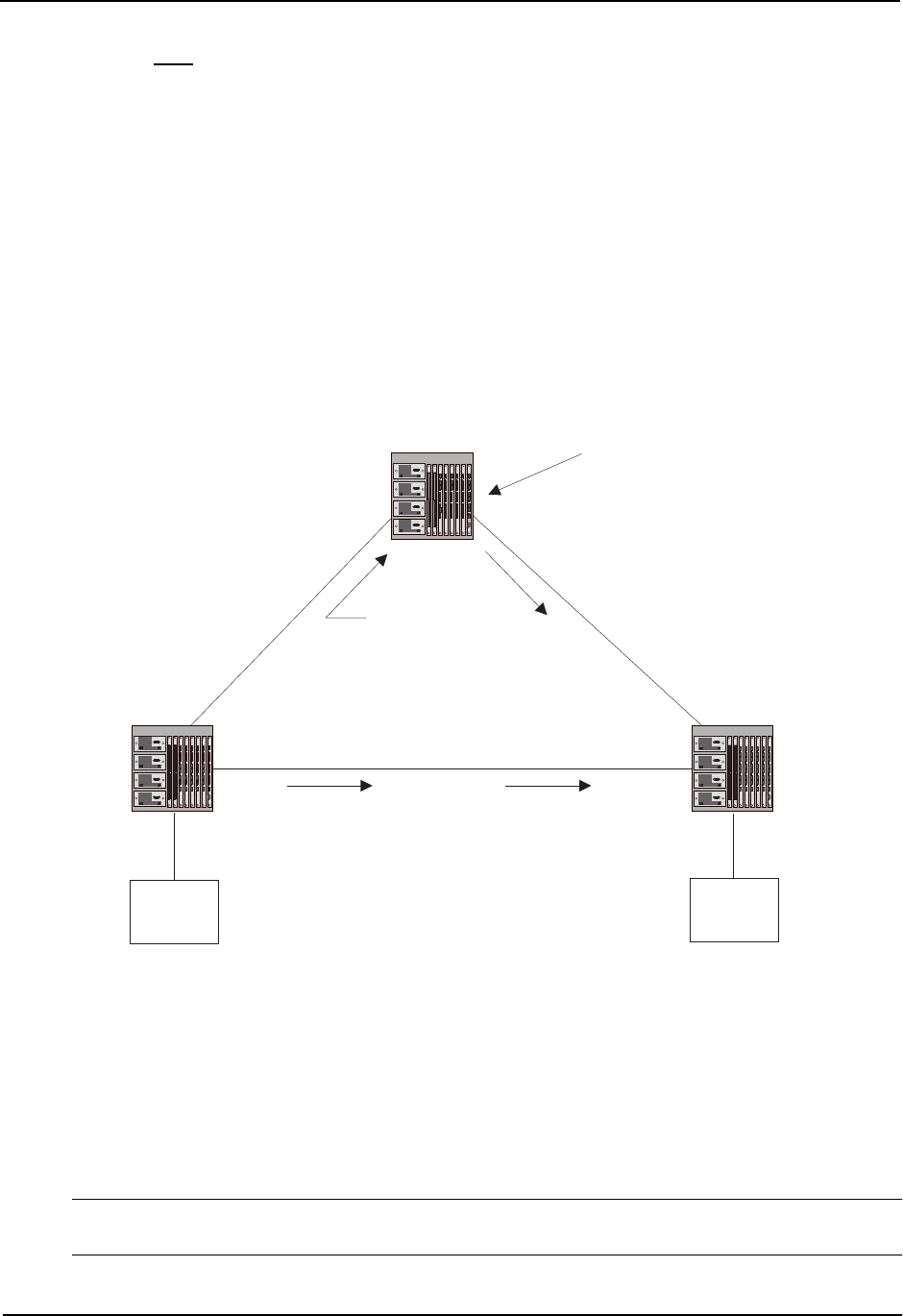
implement PIM and are configured to operate within a common boundary. Figure 9.3 shows a simple example of
a PIM Sparse domain. This example shows three HP 9304M or HP 9308M routing switches configured as PIM
Sparse routers. The configuration is described in detail following the figure.
PIM Sparse router B
This interface is also the
Bootstrap Router (BR) for
PIM Sparse router A
VE 1
207.95.6.1
Shortest Path Tree (SPT) path
209.157.24.162
Port 3/8
207.95.7.2
Rendezvous Point (RP) path
VE 1
207.95.6.2
this PIM Sparse domain, and
the Rendezvous Point (RP) for the
PIM Sparse groups in this domain.
Port 3/8
207.95.8.1
Port 2/1
207.95.8.10
Port 2/2
207.95.7.1
PIM Sparse router C
Source for Group
239.255.162.1
Receiver for Group
239.255.162.1
Figure 9.3 Example PIM Sparse domain
PIM Sparse Router Types
Routers that are configured with PIM Sparse interfaces also can be configured to fill one or more of the following
roles:
• PMBR – A PIM router that has some interfaces within the PIM domain and other interface outside the PIM
domain. PBMRs connect the PIM domain to the Internet.
NOTE: You cannot configure an HP routing interface as a PMBR interface for PIM Sparse in the current
software release.
9 - 12