Configuring VLANs
16 - 7
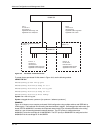
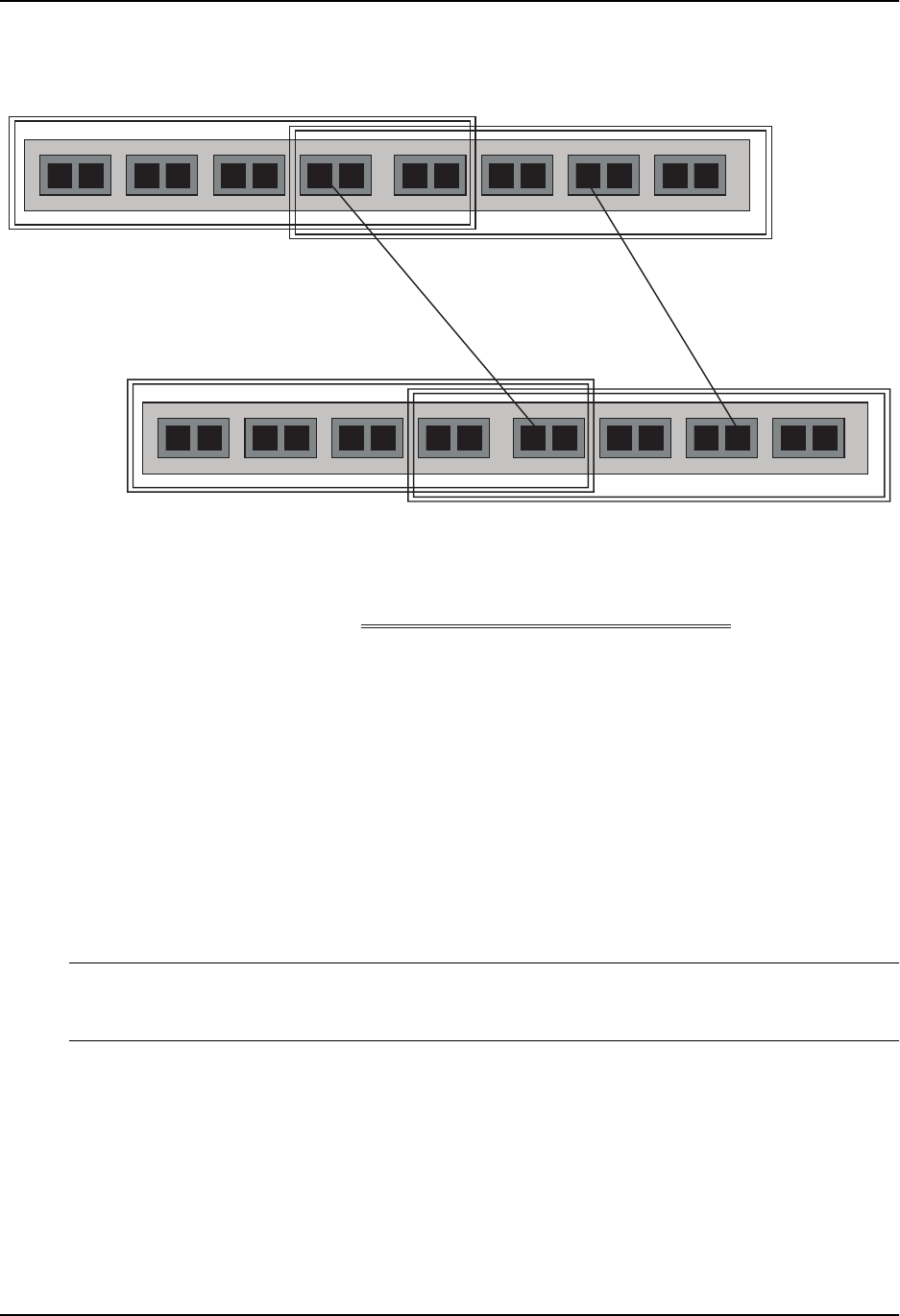
Figure 16.5 VLANs configured across multiple devices
Spanning Tree Protocol (STP)
The default state of STP depends on the device type:
• STP is disabled by default on the HP 9304M, HP 9308M, and HP 6308M-SX routing switches.
• STP is enabled by default on the HP 6208M-SX switch.
Also by default, each port-based VLAN has a separate instance of STP. Thus, when STP is globally enabled,
each port-based VLAN on the device runs a separate spanning tree.
You can enable or disable STP on the following levels:
• Globally – Affects all ports on the device.
NOTE: When you configure a VLAN, the VLAN inherits the global STP settings. owever, once you begin to
define a VLAN, you can no longer configure STP globally. om that point on, you can configure STP only
within individual VLANs.
• Port-based VLAN – Affects all ports within the specified port-based VLAN. When you enable or disable STP
within a port-based VLAN, the setting overrides the global setting. hus, you can enable STP for the ports
within a port-based VLAN even when STP is globally disabled, or disable the ports within a port-based VLAN
when STP is globally enabled.
STP is a Layer 2 protocol. Thus, you cannot enable or disable STP for individual protocol VLANs or for IP sub-
net, IPX network, or AppleTalk cable VLANs. The STP state of a port-based VLAN containing these other types of
VLANs determines the STP state for all the Layer 2 broadcasts within the port-based VLAN. This is true even
though Layer 3 protocol broadcasts are sent on Layer 2 within the VLAN.
It is possible that STP will block one or more ports in a protocol VLAN that uses a virtual interface to route to other
VLANs. ocol and IP sub-net VLANs, even though some of the physical ports of the virtual interface are
User-configured port-basedVLAN
VLAN A VLAN A/B VLAN B
VLAN A VLAN A/B VLAN B
Segment 1
Segment 2
H
Fr
T
For IP prot