1-6
Cisco VISM Installation and Configuration Guide
Release 3.0, Part Number OL-2521-01 Rev. D0, June 2004
Chapter 1 Overview of the VISM and VISM-PR Cards
VISM and VISM-PR Card Features
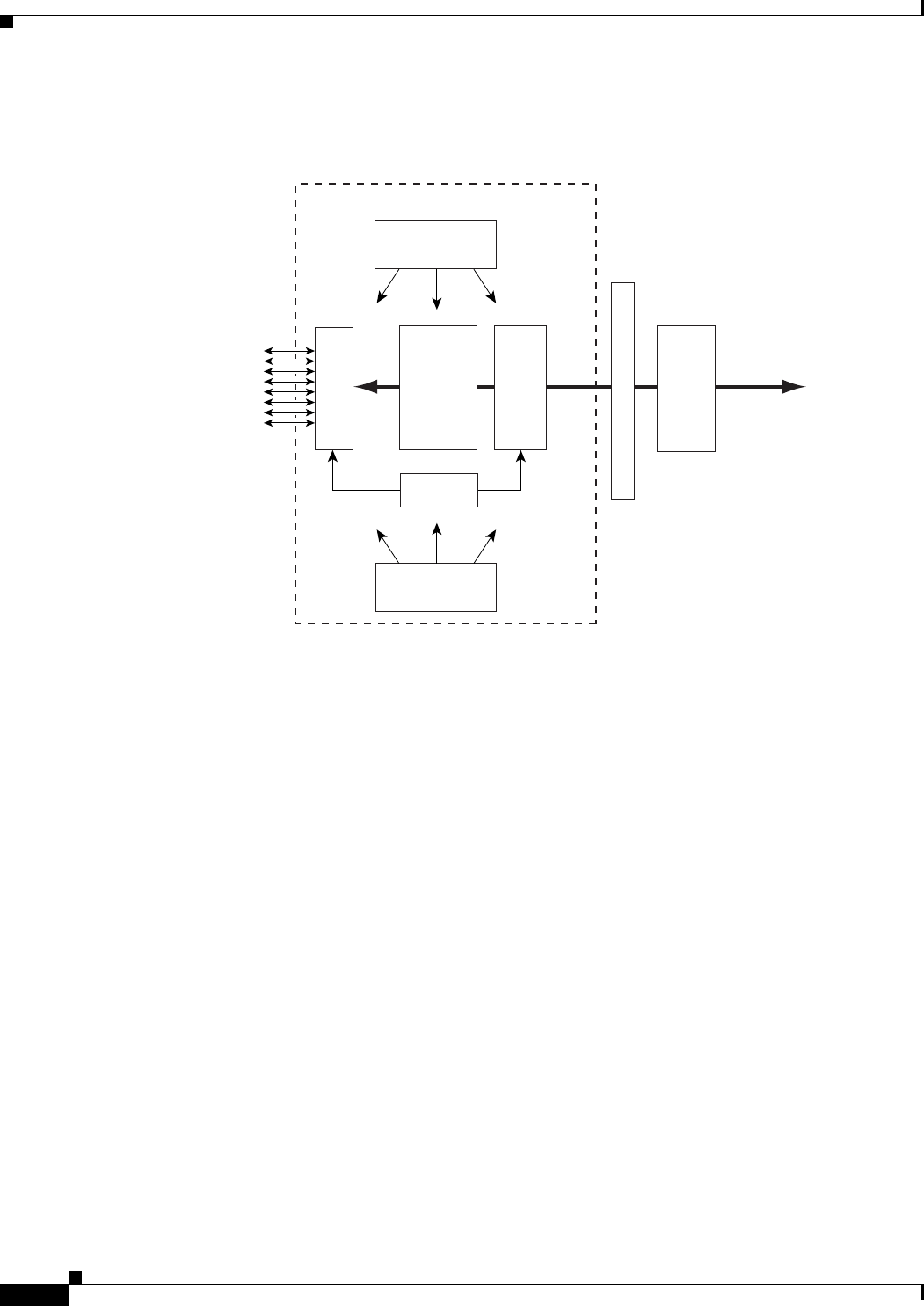
Figure 1-5 shows a simplified diagram of the VISM architecture and its major components.
Figure 1-5 VISM Card Block Diagram
The card is broadly divided into a TDM side and an ATM side. The T1/E1 framers, the array of DSPs,
and the HDLC processor support the TDM side. The ATM adaptation layer (AAL) and the segmentation
and reassembly (SAR) sections support the ATM side.
VISM is under the control of two independent processors. The main processor performs the control
tasks—configuration, call setup and teardown, and management. The second processor, the datamover,
handles the moving and processing of the voice and voiceband data traffic through the system.
The VISM card itself contains no ports for the connection of management stations. Workstations, PCs,
or terminals used to manage VISM must be attached via the PXM card which provides both serial
EIA/TIA-232 and Ethernet ports.
VISM and VISM-PR Card Features
VISM cards process high-density digital voice circuits and provide dynamic compression, echo
cancellation, dejittering, silence suppression, and packetization. The VISM card uses the following
features which you can configure:
• Eight standard T1 or E1 interfaces with the following line coding:
–
Bipolar 8-zero substitution (B8ZS)—for T1
–
Alternate mark inversion (AMI)—for T1
–
High density bipolar 3 (HDB3)—for E1
8 T1/E1 lines
from PBX or
C
entral Office
Digital
Signal
Processors
SAR
Cellbus
PXM
OC-3 to ATM
Packet Netwo
rk
Framers
Main CPU
(Control)
Secondary CPU
(Datamover)
VISM
HDLC
Processor
3
1429