1-11
Cisco VISM Installation and Configuration Guide
Release 3.0, Part Number OL-2521-01 Rev. D0, June 2004
Chapter 1 Overview of the VISM and VISM-PR Cards
VISM and VISM-PR Card Features
Call Agent Interface
The call agent interface consists of CAS signaling or CCS signaling and call control. The path between
the call agent and bearer processing, via a connection handling function, is for call setup and teardown.
The CAS signaling path on the TDM side is embedded in the voice stream (bearer DS0s) and is separated
at the bearer processing function. The CAS signaling (robbed bits, digits, and tones) is passed to the
CAS/CCS processing function where it is passed (backhauled) to the call agent under the control of the
call agent. The mechanism for communicating between VISM and the call agent is a gateway control
protocol:
• MGCP
• SGCP
• SRCP
The separate CCS signaling path channels are passed to the CAS/CCS processing function and
backhauled to the call agent. The CCS signaling is transported as ISDN Q.931 messages both on the
TDM side and on the call agent side. On the TDM side, the messages are carried in the Q.921 layer
protocol (which terminates at the VISM card). On the call agent side, communication with the call agent
consists of Q.931 messages encapsulated in RUDP/UDP/IP packets. The Q.931 connection is terminated
at the call agent and not at the VISM card.
The call control path uses MGCP, SGCP, and SRCP for call setup and teardown. Because signaling and
call control are so intertwined, both call control and CAS use the same path and protocol for the VISM
card to call agent communications.
AAL2 Trunking Operating Mode
In the AAL2 trunking operating mode, the VISM card serves as an access to one or more trunks to
preprovisioned locations. VISM may be used at both ends of the trunk, or at one end with a compatible
device at the other. In AAL2 trunking mode, VISM plays no part in call setup and teardown. Other
network elements handle call control while VISM merely handles voice transport over the trunks.
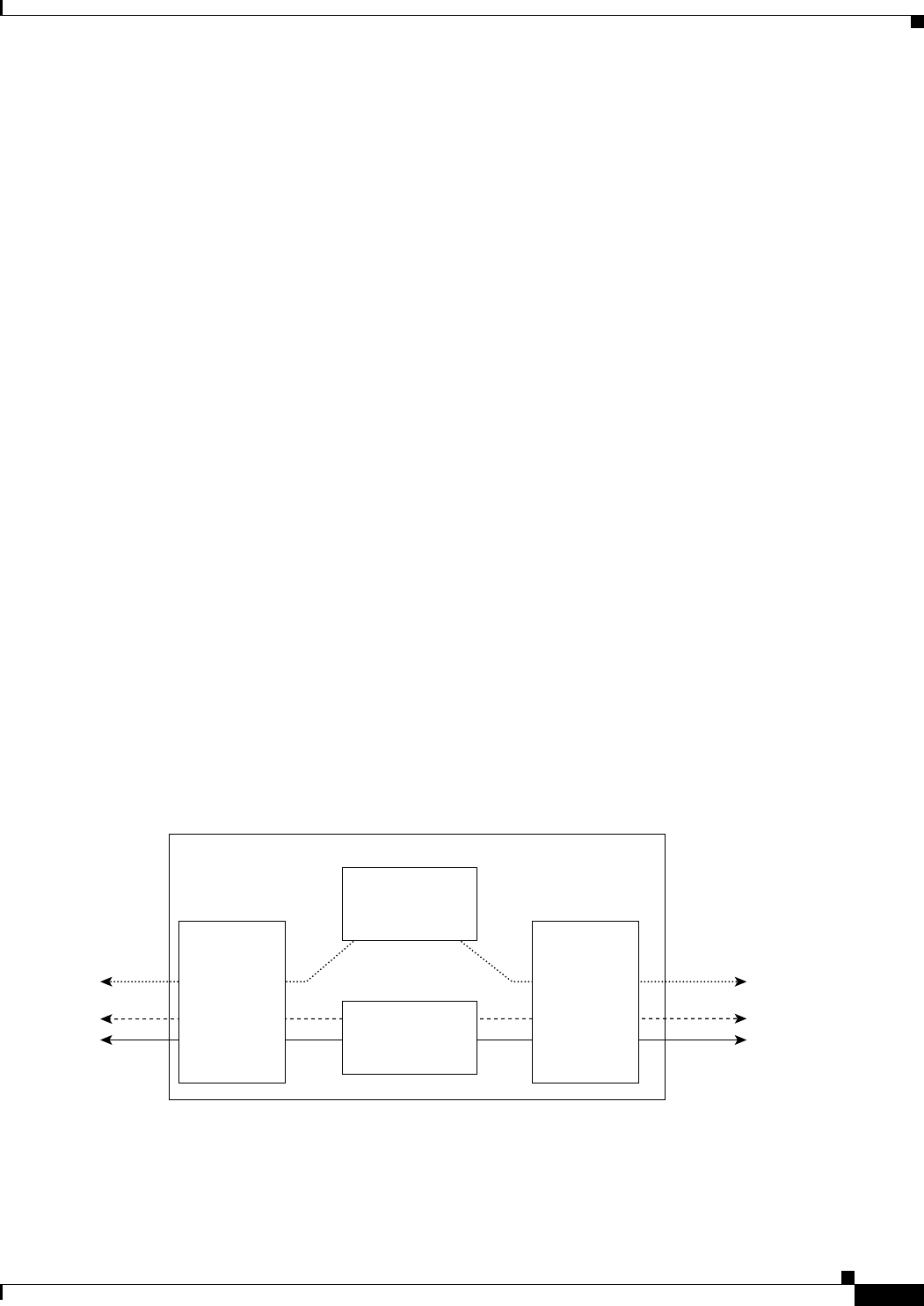
Figure 1-7 shows the major functional blocks for the AAL2 trunking operating mode.
Figure 1-7 VISM Block Diagram for the AAL2 Trunking Operating Mode
The AAL2 trunking mode is less complex than the VoIP switching and AAL2 PVC switched modes
because there is no call control involved—and no need for a call agent.
TDM Line
Handling
ATM
Processing
CCS
Processing
To ATM
Trunk
CCS
CCS
CAS
CAS
Voice
VISM
Voice
5
3232
T
1/E1 Lines
Bearer
Processing