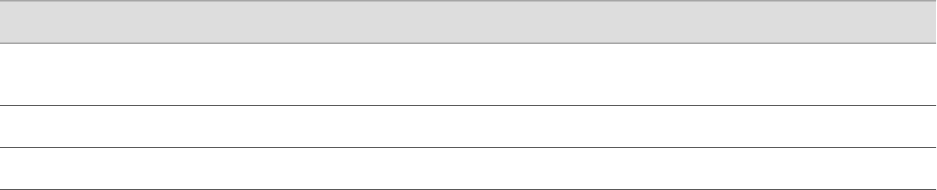
Table 41: Interfaces and Protocols for IP Address Acqusition During Autoinstallation
Protocol for AutoinstallationInterface and Encapsulation Type
DHCP, BOOTP, or Reverse Address Resolution Protocol
(RARP)
Ethernet LAN interface with High-level Data Link Control (HDLC)
Serial Line Address Resolution Protocol (SLARP)Serial WAN interface with HDLC
BOOTPSerial WAN interface with Frame Relay
If the server with the autoinstallation configuration file is not on the same LAN
segment as the new Services Router, or if a specific router is required by the network,
you must configure an intermediate router directly attached to the new router, through
which the new router can send Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP), BOOTP, and
Domain Name System (DNS) requests. In this case, you specify the IP address of the
intermediate router as the location to receive TFTP requests for autoinstallation.
Typical Autoinstallation Process on a New Services Router
When a Services Router is powered on for the first time, it performs the following
autoinstallation tasks:
1. The new Services Router sends out DHCP, BOOTP, RARP, or SLARP requests on
each connected interface simultaneously to obtain an IP address.
If a DHCP server responds, it provides the router with some or all of the following
information:
■ An IP address and subnet mask for the autoinstallation interface.
■ The location of the TFTP (typically), Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP), or
FTP server on which the configuration file is stored.
■ The name of the configuration file to be requested from the TFTP server.
■ The IP address or hostname of the TFTP server.
If the DHCP server provides only the hostname, a DNS server must be
available on the network to resolve the name to an IP address.
■ The IP address of an intermediate router if the configuration server is on a
different LAN segment from the new router.
Autoinstallation Overview ■ 83
Chapter 5: Configuring Autoinstallation


















