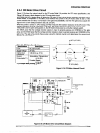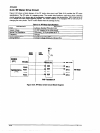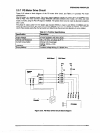
2.3.9 Printhead Drive Circuit
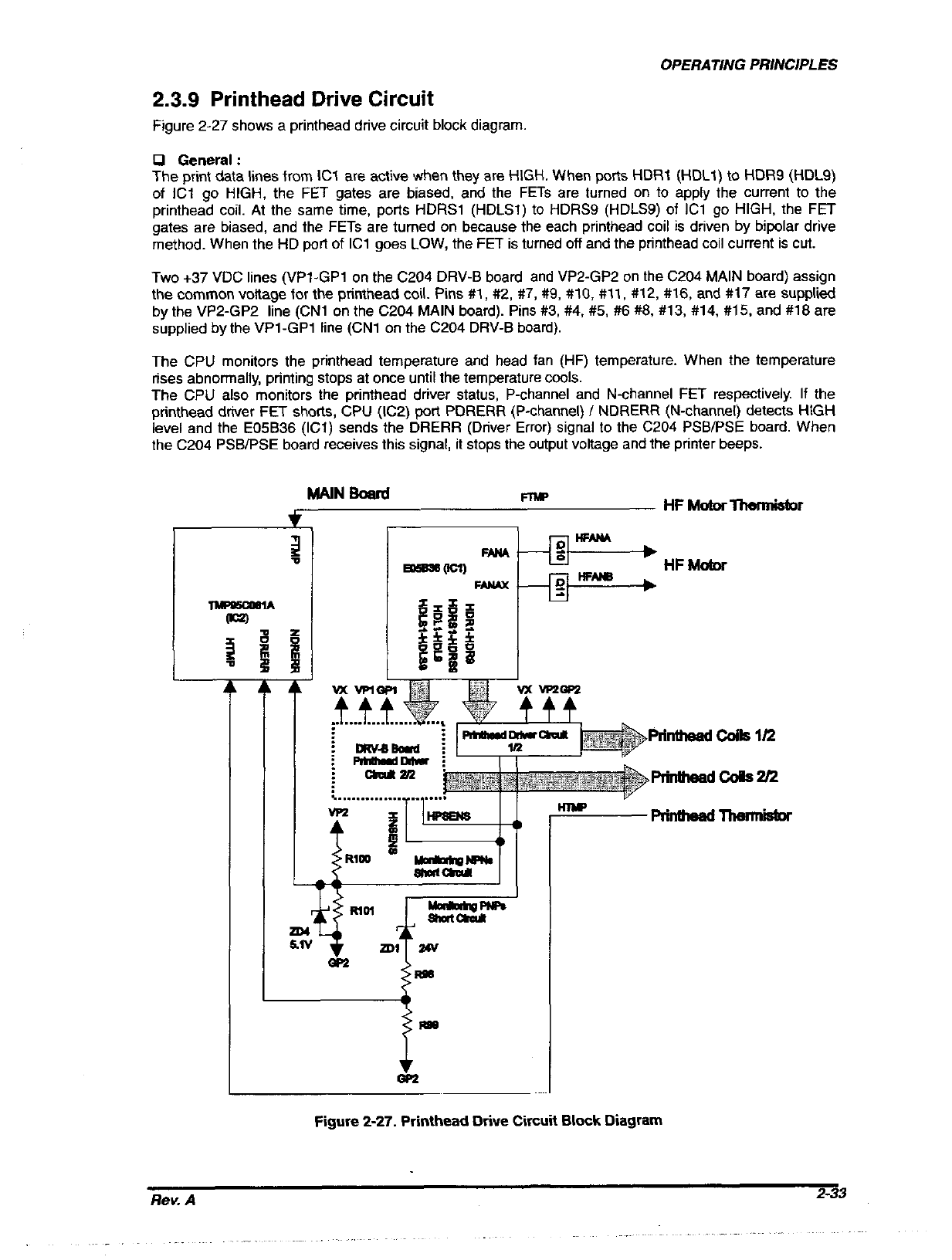
Figure 2-27 shows a printhead drive circuit block diagram.
0 General:
The print data lines from ICl are active when they are HIGH. When ports HDRI (HDLl) to HDR9 (HDLS)
of ICl go HIGH, the FET gates are biased, and the FETs are turned on to apply the current to the
printhead coil. At the same time, ports HDRSl (HDLSl) to HDRSS (HDLSS) of ICl go HIGH, the FET
gates are biased, and the FETs are turned on because the each printhead coil is driven by bipolar drive
method. When the HD part of ICl goes LOW, the FET is turned off and the printhead coil current is cut.
Two +37 VDC lines (VPl-GPl on the C204 DRV-B board and VP2-GP2 on the C204 MAIN board) assign
the common voltage for the printhead coil. Pins #l, #2, #7, #9, #lo, #ll, #12, #16, and #17 are supplied
by the VP2-GP2 line (CNl on the C204 MAIN board). Pins #3, #4, #5. #6 #8. #13, #14, #15, and #18 are
supplied by the VPl-GPl line (CNl on the C204 DRV-B board).
The CPU monitors the printhead temperature and head fan (HF) temperature. When the temperature
rises abnormally, printing stops at once until the temperature cools.
The CPU also monitors the printhead driver status, P-channel and N-channel FET respectively. If the
printhead driver FET shorts, CPU (IC2) port PDRERR (P-channel) I NDRERR (N-channel) detects HIGH
level and the E05B36 (IGl) sends the DRERR (Driver Error) signal to the C204 PSBiPSE board. When
the C204 PSB/PSE board receives this signal, it stops the output voltage and the printer beeps.
MAlNBOd
Frw
HFMotwThemMor
Figure 2-27. Printhead Drive Circuit Block Diagram
Rev. A
2-33