Chapter 2 Configuration and Installation
AT-MIO-16X User Manual 2-4
©
National Instruments Corporation
The base address DIP switch is arranged so that a logical 1 or true state
for the associated address selection bit is selected by pushing the toggle
switch up, or toward the top of the board. Alternately, a logical 0 or
false state is selected by pushing the toggle switch down, or toward the
bottom of the board. In Figure 2-3B, A9 is up (true), A8 through A6
are low (false), and A5 is up (true). This represents a binary value of
10001XXXXX, or hex 220. The Xs indicate don’t care bits and are the
five least significant bits (LSBs) of the address (A4 through A0) used
by the AT-MIO-16X circuitry to decode the individual register
selections. The don’t care bits indicate the size of the register space. In
this case, the AT-MIO-16X uses I/O address hex 220 through hex 23F
in the factory-default setting.
Note: If you change the AT-MIO-16X base I/O address, you must make a
corresponding change to any software packages you use with the
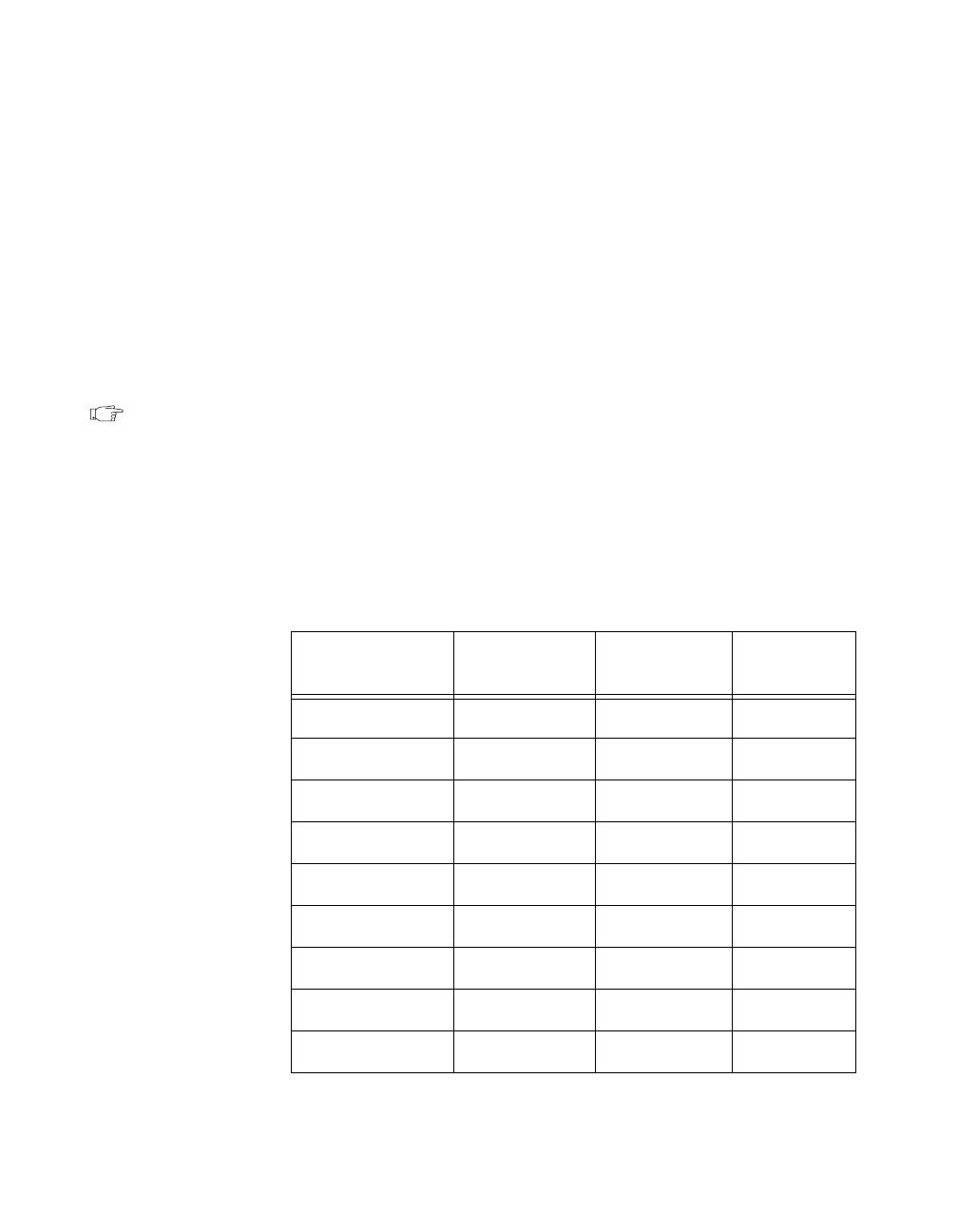
AT-MIO-16X. Table 2-1 lists the default settings of other National
Instruments products for the PC. Table 2-2 lists the possible switch
settings, the corresponding base I/O address, and the base I/O address
space used for that setting. For more information about the I/O address
of your PC, refer to the technical reference manual for your computer.
Table 2-1. Default Settings of National Instruments Products for the PC
Board DMA
Channel
Interrupt
Level
Base I/O
Address
AT-A2150 None* None* 120 hex
AT-AO-6/10 Channel 5 Lines 11, 12 1C0 hex
AT-DIO-32F Channels 5, 6 Lines 11, 12 240 hex
AT-DSP2200 None* None* 120 hex
AT-GPIB Channel 5 Line 11 2C0 hex
AT-MIO-16 Channels 6, 7 Line 10 220 hex
AT-MIO-16D Channels 6, 7 Lines 5, 10 220 hex
AT-MIO-16F-5 Channels 6, 7 Line 10 220 hex
AT-MIO-16X None* None* 220 hex


















