Chapter 3 Theory of Operation
AT-MIO-16X User Manual 3-14
©
National Instruments Corporation
Interval Scanning Data Acquisition Timing
Interval scanning assigns a time between the beginning of consecutive
scan sequences. If only one scan sequence is in the configuration
memory list, the circuitry stops at the end of the list and waits the
necessary interval time before starting the scan sequence again. If
multiple scan sequences are in the configuration memory list, the
circuitry stops at the end of each scan sequence and waits the necessary
time interval before starting the next scan sequence. When the end of
the scan list is reached, the circuitry stops and waits the necessary time
interval before sequencing through the channel information list again.
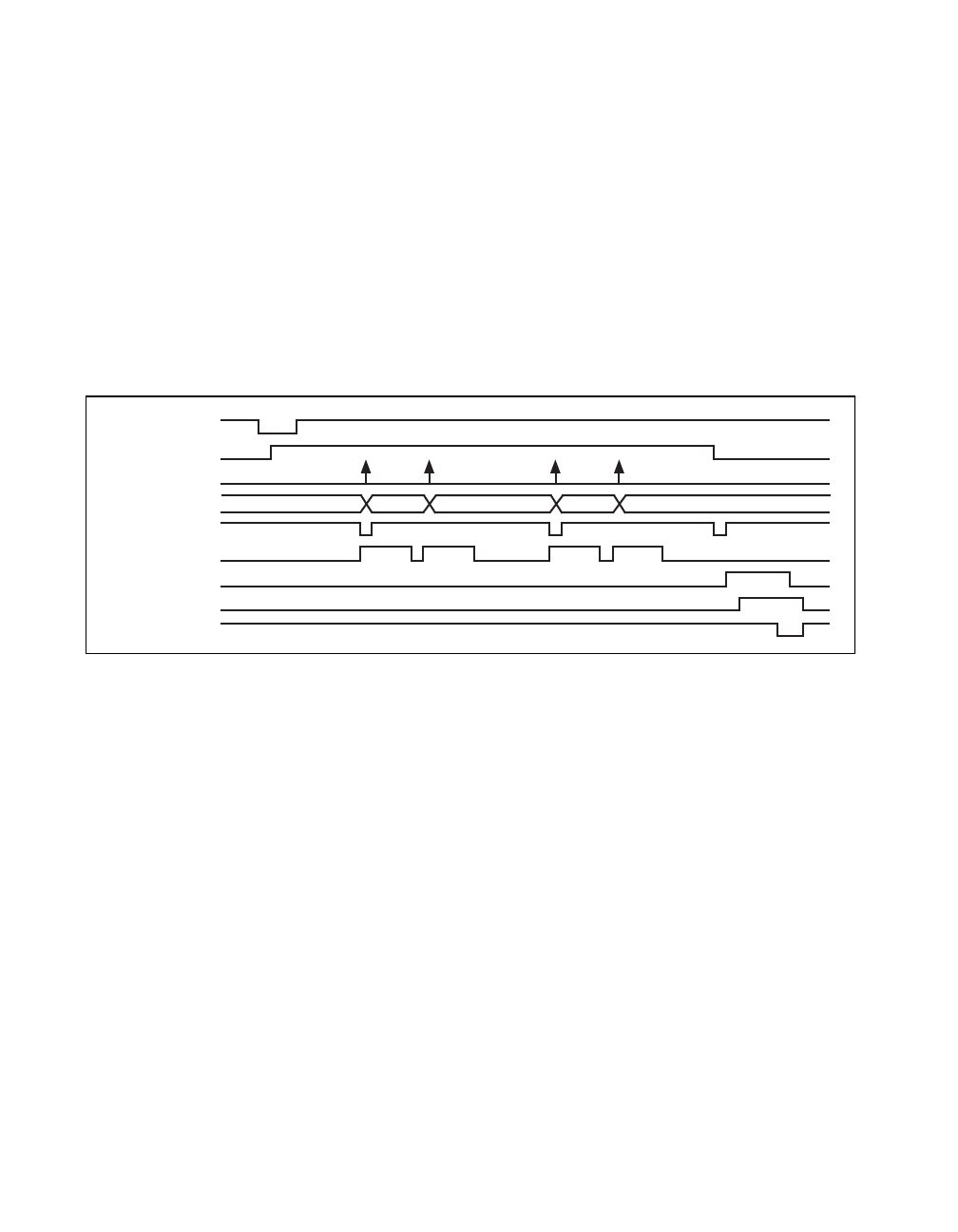
Figure 3-8 shows an example of the interval scanning sequence timing.
Figure 3-8.
Interval Scanning Posttrigger Data Acquisition Timing
In interval-scanning applications, the first sample does not occur until
after the first falling edge of the Counter 2 output, or one scan interval
after the trigger. Scanning stops at the end of the first scan sequence or
at the end of the entire scan list. The sequence restarts after a rising edge
on Counter 2 is detected. The interval-scanning mode is useful for
applications where a number of channels need to be monitored over a
long period of time. Interval-scanning monitors the N channels every
scan interval, so the effective channel conversion interval is equal to the
interval between scans.
Trigger*
DAQPROG
DAQCMPLT
DAQCLEAR*
Interrupt
Channel
SCANCLK
COUNTER2
CONVERT
01 0 10