Release 1.0, 1 July 2002 F. Chapter L Address Space Identifiers 121
n = 2 (4-byte alignment): LDDF_mem_address_not_aligned exception is
generated.
n ≤ 1 (≤ 2-byte alignment): mem_address_not_aligned exception is generated.
2. If the memory address is correctly aligned, SPARC64 V generates a
data_access_exception with AFSR.FTYPE = “invalid ASI.”
L.4 Barrier Assist for Parallel Processing
SPARC64 V has a barrier-assist feature that works in concert with the barrier mechanism in
the memory system to enable high-speed synchronization among CPUs in the system.
Barrier assist is highly dependent on the barrier mechanism in the memory system.
A description of the barrier mechanism is beyond the scope of this supplement; see
appropriate system documents for details.
L.4.1 Interface Definition
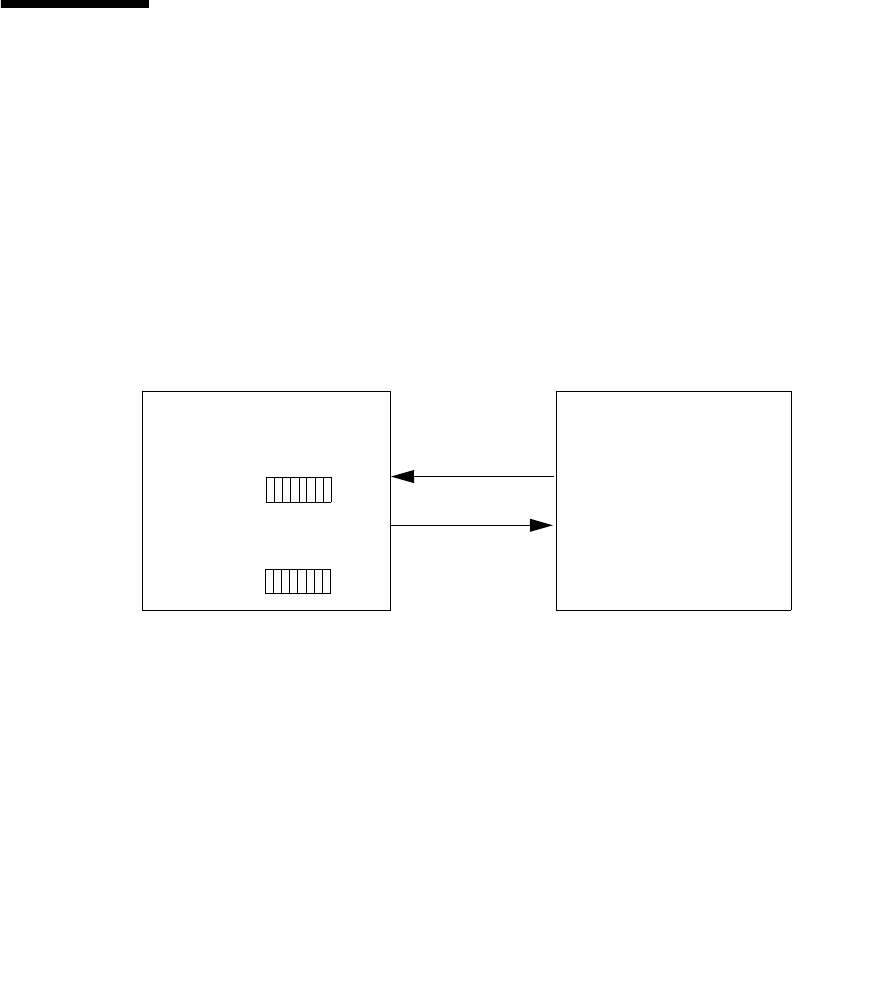
FIGURE L-4
illustrates the interface between CPU and the memory system.
FIGURE L-4
CPU Interface of Barrier Assist
High-Speed LBSY Read Mechanism
1. The CPU has a copy of LBSY in the system. Two LBSYs exist on a system board
(SB), SB_BPU#0 and SB_BPU#1. Each LBSY is 8 bits wide. The copy of LBSY
residing in the CPU is 16 bits.
2. On power-on reset, both the LBSY copy in the CPU and the LBSY copies on the SB
are cleared.
LBSY change info
BST write info
CPU
SB
Copy of SB_BPU#0 LBSY
7
0
Copy of SB_BPU#1 LBSY
0
7


















