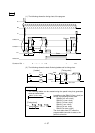
5 - 1
CHAPTER 5 BASIC INSTRUCTION -PART 2-
5.1 Notation of Values (Data)
The programmable controller CPU converts all input signals into ON or OFF signals
(logical 1 or 0, respectively) to store and process them. Therefore, the
programmable controller executes the numeric operation using the numeric values
stored with the logical 1 or 0 (binary numbers = BIN).
In daily life, a decimal number is regarded as the most commonly and the easiest
system. Therefore, the decimal-to-binary conversion or the reverse conversion is
required when values are written or read (monitored) to or from the programmable
controller. The programming system and some instructions have the function for the
decimal-to-binary conversion and the binary-to-decimal conversion.
This section explains how to express values (data) in decimal, binary, hexadecimal
and binary-coded decimal notation (BCD), and how to convert them.
Decimal
A decimal number system consists of ten symbols: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, and 9
which represent the order and size (amount).
After a digit reaches 9, an increment is reset to 0 and the next increment of the
next digit (to the left) is incremented.
The following shows how a decimal number (in this case 153) is represented.
153 = 100+50+3
= 1
100+5
10+3
1
= 1
10
2
+
5 10
1
+
3 10
0
Decimal symbol (0 to 9)
"Power of digit"
n : Digit number (0, 1, 2...)
10 : Decimal
In the MELSEC-Q series programmable controller, symbol "K" is used for
expressing values in decimal.