App. - 25
Appendix 4.18 Application example of (D) C M L
Complement
(P)
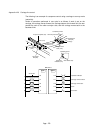
The following explains how to obtain absolute values of negative values -32768 or
smaller (to -2147483648, 32 bit data).
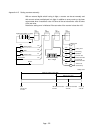
DCML D20
D+
D20
D0
K1
1011 0100011 10010
B
15
B
14
B
1
B
0
B
15
B
14
B
1
B
0
D1
D0
0100 1011100 01101
0100 1011100 01110
D21 D20
D21 D20
(Negative number)
(Absolute value)
Before DCML
execution
After DCML
execution
After D+ execution
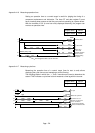
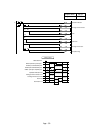
(Example)
Every time X1 is turned on, 999 is subtracted from a set value and the result is
displayed.
When the result value is negative, the output Y70 turns on, and the absolute value of
the result is displayed.
Reading the set value
Subtraction (-999)
Negative number
obtained?
Y70 setting
DCML execution
+1 execution
Result display
NO
YES
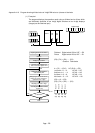
Turn on X0
Turn on X1
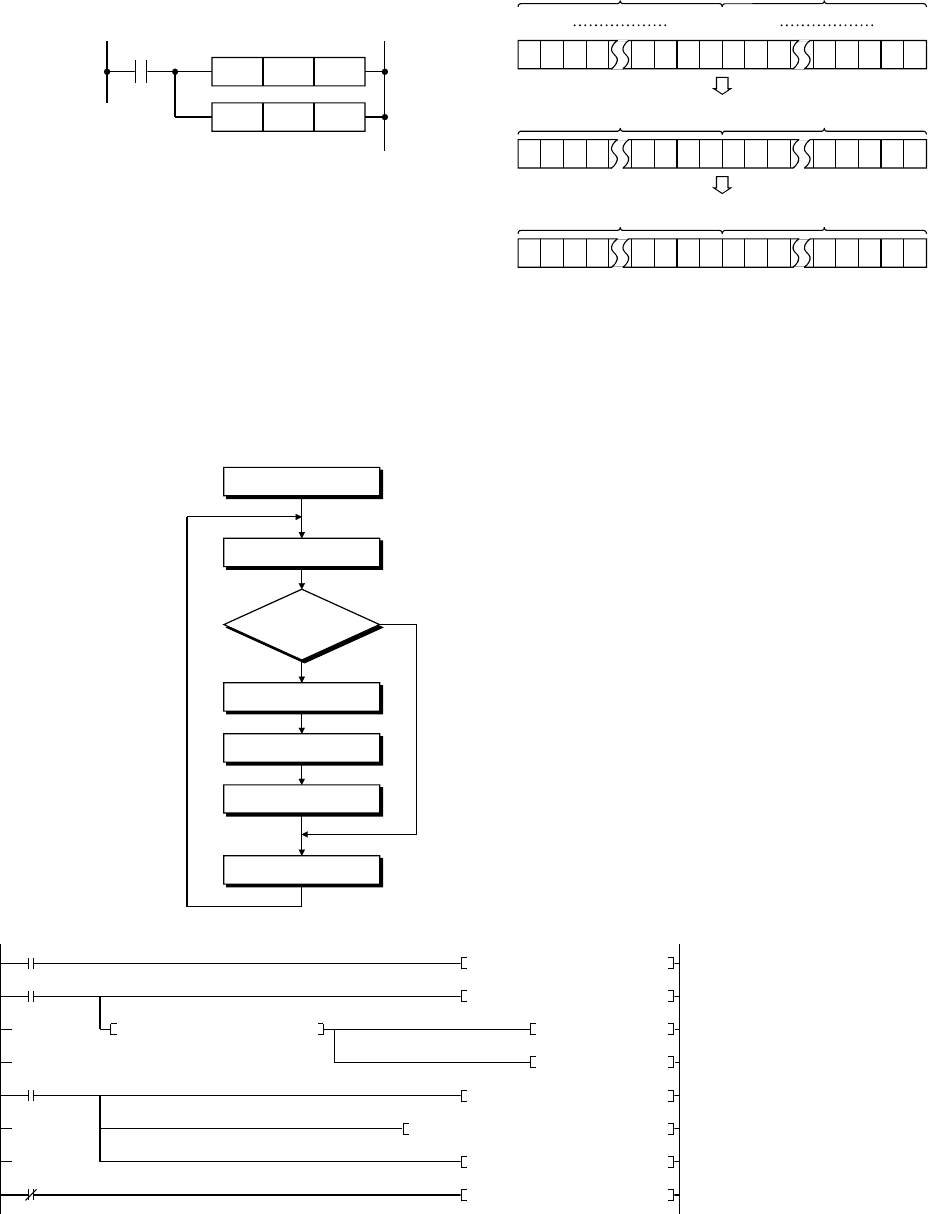
X0
X1
M0
Y70
D0K4X20DBIN
0
4
18
31
Inputs data
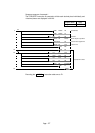
D0K0D> Y70SET
M0
PLS
D0K999D-P
D20D0DCML
D30K1
K8Y40D30DBCD
K8Y40D0DBCD
D+ D20
Subtracts 999
Turns on Y70 when
negative number is obtained
When D0 is negative number,
two's complement is taken to
have positive number (absolute value)
Outputs absolute value
Outputs positive number