5 - 25
Reference
If
D
is a bit device, the operation becomes as follows;
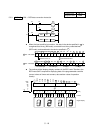
FMOV instruction
Input
condition
DS
K4K2Y40D0FMOV
n
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 01
S
D0 (Example: when the content is 365)
As specifies
a two-digit number,
these data are
ignored.
D
0 1 1 0 1 1 01
Y48Y4F
D
0 1 1 0 1 1 01
Y40Y47
D
0 1 1 0 1 1 01
Y58Y5F
D
0 1 1 0 1 1 01
Y50Y57
D
n
4 devices (K4)
Among the device of Y40 to Y5F, the devices specified as "1" are output first.
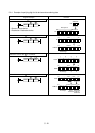
In the program shown below, turning on the input condition 1) turns on all the
outputs Y40 to Y5F and turning on the input condition 2) turns them off.
Input
condition 1)
K4K2Y40K255FMOV
0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 11
Input
condition 2)
K4K2Y40K0FMOV
Bit pattern of K255
In units of four bits, to turn off;
16 bit devices or less MOV instruction Example
32 bit devices or less
DMOV instruction Example
More than 32 bit devices
FMOV instruction Example
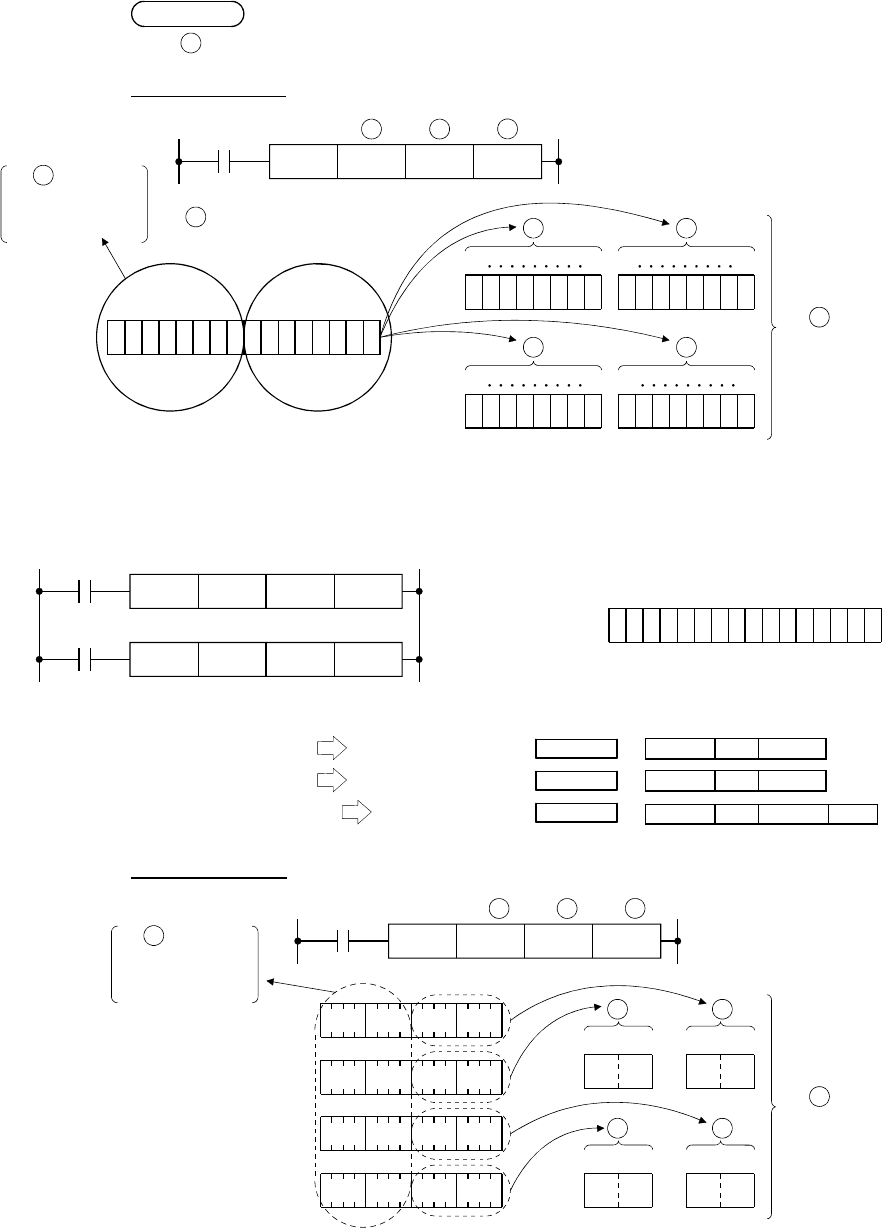
BMOV instruction
Input
condition
DS
K4K2Y40D0BMOV
n
5
Y48
n
4 devices (K4)
7
Y4F
5
Y40
1
Y47
5
Y58
5
Y5F
5
Y50
6
Y57
3 0 5 1D0
3 0 5 7D1
3 0 5 6D2
3 0 5 5D3
As specifies
a two-digit number,
these data are
ignored.
D
D D
D D
In the example above, the devices D0 to D3 store the product code (16 bits). The
BMOV instruction is useful for displaying and monitoring the last two digits
representing their types.
MOV K0 K4M0
DMOV K0 K8M0
FMOV K0 K4M0 K4
(Turns off 64 bit devices)