5 - 37
2
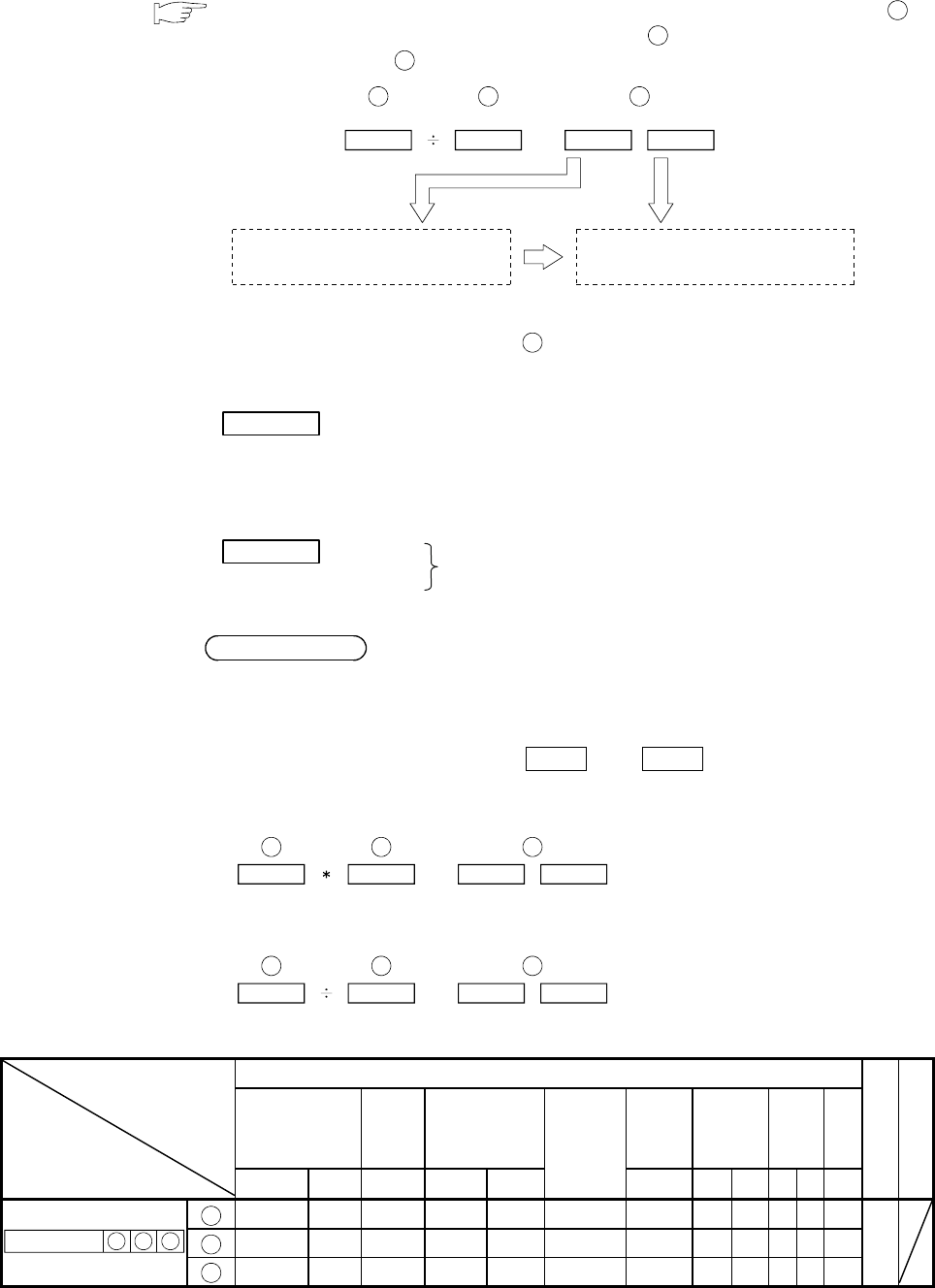
● When the input condition is turned on, the content of the device specified in
S1
is
divided by the content of the device specified in
S2
and the result is stored in the
device specified in
D
.
D0
2000
S1
K600
600
S2
=
D20 D21
D
3
The quotient is stored to D20, which is
specified in the program.
200
The remainder is stored to D21, which
is the next device number.
and
Quotient Remainder
Values after the decimal point of the operation result are ignored.
● When a bit device is specified in
D
, the quotient is stored, but the remainder is
not stored.
● The following shows examples for processing negative values.
Example
-5 / (-3) = 1, remainder: -2
5 / (-3) = -1, remainder: 2
● The following shows examples for dividing a number by 0, or dividing 0 by a
number.
Example
0 / 0
1 / 0
0 / 1, Both quotient and remainder are 0.
Operation Practice
● Write the program to the CPU and run it.
● Turn on X0 and store "2000" (BIN value) in D0.
● Turn on X2. The following operation is executed.
If "60000" (operation result of D11 and D10 is regarded as a 16-bit
integral number and only D10 is monitored, "-5536" is displayed. To prevent this,
follow the procedures in the following pages.
(30)
K30
S1
(2000)
D0
S2
=
(60000)
D
D11 D10
● Turn on X3.
(2000)
D0
S1
(600)
K600
S2
=
(3)
D
D21 D20
(200)
QuotientRemainder
Applicable device
Internal device
(system or
user)
File
register
MELSECNET/
10 (H) Direct
Jn\
Index
register
Constant
Pointer
Level
Bit Word R Bit Word
Intelligent
function
module
Un\G
Z K H P I N
Digit
Number of basic
ste
p
s
S1
S2
S1
Multiplication/division
instruction
DS2
D
K1
to
K4
*
4
The number of basic steps for the multiplication instruction is three or four, and that for division instruction is four.
*: The multiplication instruction varies depending on the device to be used.
Error "OPERATION ERROR"