7-5
[Transmission character string]
Transmission character strings are classified as follows. The details about the @ commands and parameter
commands will be explained separately in Section 7.4, “@ Commands” and Section 7.5, “Parameter
Commands.”
Explanation Receivable status
@ commands Commands for operating the driver
Receivable status changes
depending on the command.
Parameter
commands
Commands for setting parameters and
reading parameter/monitor values.
Receivable status changes
depending on the parameter.
[Response character string]
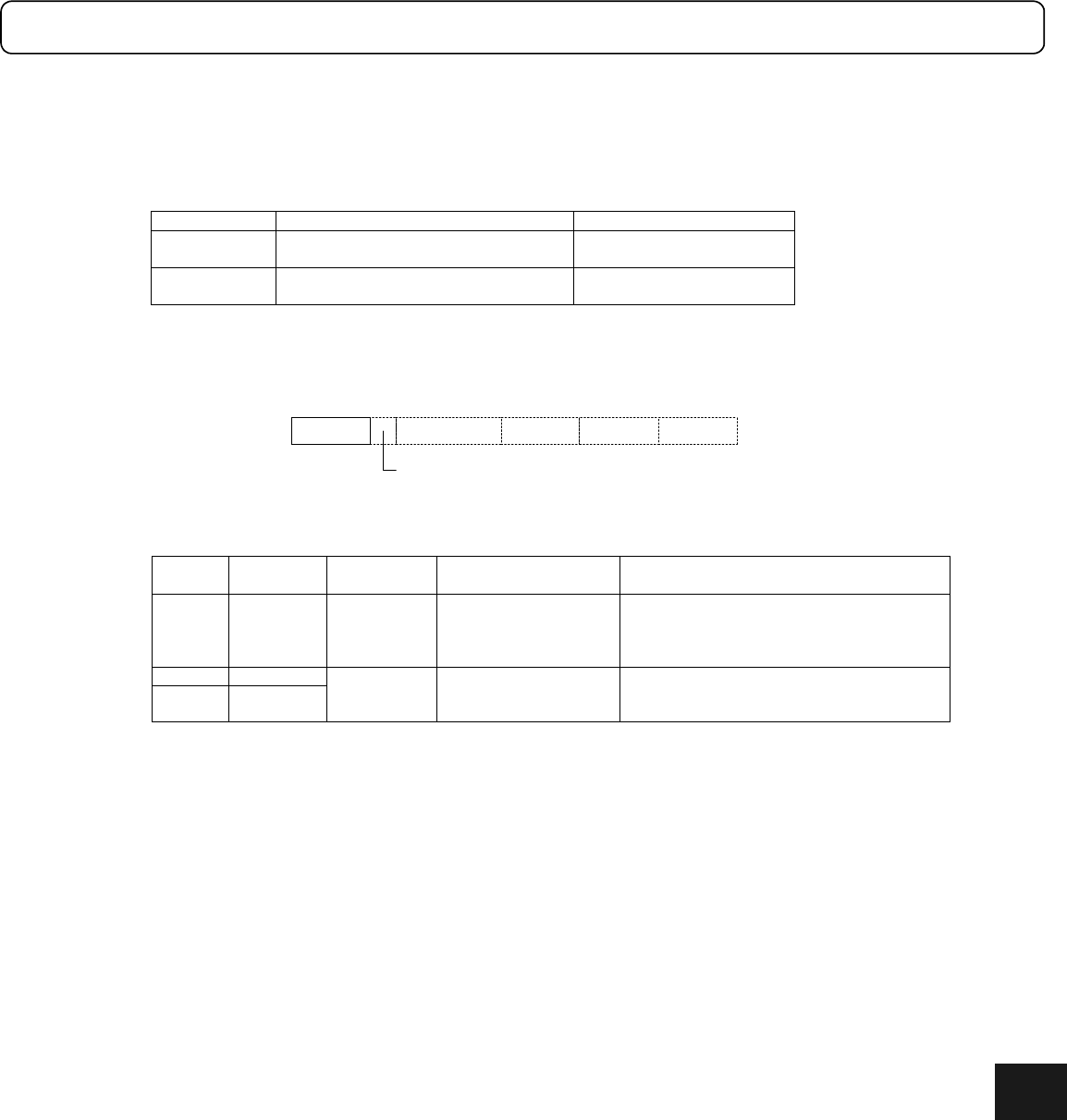
A response character string is structured as follows.
: Field 1
Response
character string
Prompt : Field 2
...
: Field 3
Space, one character
Header
Response character strings are classified as follows.
Header
structure
! part " part Explanation
General R!"
Number of
fields
For the field expression
method; see the note.
Normal response character strings to a
transmission character string.
The number of fields changes depending on
the content of the response.
Error ERR!!."
Alarm ALM!!."
Error/alarm
code (main)
Error/alarm code (sub)
Response character string to a transmission
character string at error and alarm.
Fields never exists.
Note: In case of a general response the " part of the field is expressed in one of the following ways:
0: In case there is no field
D: Character string expressed in decimal
B: Binary expression (8, 16, 32 digits)
H: Hexadecimal expression (2, 4, 8 digits)
S: Character string
Z: Other than above (character string, etc.)
The following shows some examples of response character strings.
R00
R1D Position control bandwidth: 12
R1B Sensor group signal status: 00010000
ERR30.0 Servo not ready
ALM60.0 Cannot interpret command
7