System Control Coprocessor
ARM DDI 0363E Copyright © 2009 ARM Limited. All rights reserved. 4-70
ID013010 Non-Confidential, Unrestricted Access
Note
The nVAL Cache Size Override Register can only be used to select cache sizes for which the
appropriate RAM has been integrated. Larger cache sizes require deeper data and tag RAMs,
and smaller cache sizes require wider tag RAMs. Therefore, it is unlikely that you can change
the cache size using this register except using a simulation model of the cache RAMs.
4.2.29 Correctable Fault Location Register
The Correctable Fault Location Register (CFLR) indicates the location of the last correctable
error that occurred during cache or TCM operations. It is not updated on speculative accesses,
for example, an instruction fetch for an instruction that is not executed because of a previous
branch. This register is:
• a read/write register
• accessible in Privileged mode only.
Note
This register is implemented from the r1pm releases of the processor. Attempting to access this
register in r0pm releases of the processor results in an Undefined Instruction exception.
The processor updates this register regardless of whether an abort is taken or an access is retried
in response to the error.
This register is updated on:
• parity or ECC errors in the instruction cache
• single-bit ECC errors in the data cache
• parity or multi-bit errors in the data cache when write-through behavior is forced
• single-bit TCM ECC errors.
The CFLR is not updated on a TCM external error or external retry request.
Every correctable error that causes a CFLR update also has an associated event. See Table 6-1
on page 6-2 for the events which are related to CFLR updates. If two correctable errors occur
simultaneously, for example an AXI slave error and an LSU or PFU error, the LSU or PFU write
takes priority. If multiple errors occur, the value in the CFLR reflects the location of the latest
event.
The same register is updated by all correctable errors. You can read bits [25:24] to determine
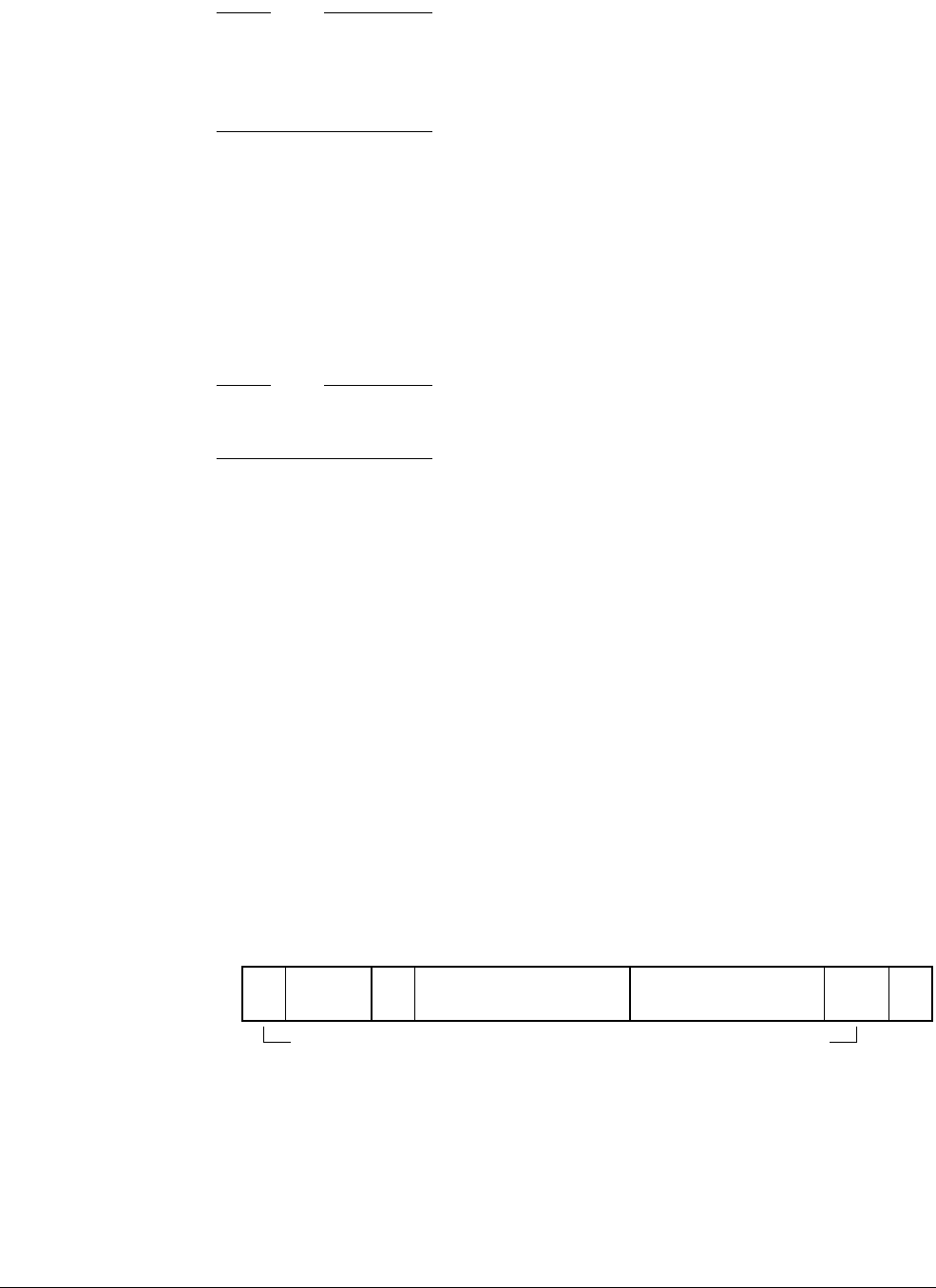
whether the error was from a cache or TCM access. Figure 4-53 shows the bit arrangement of
the CFLR when it indicates a correctable cache error.
Figure 4-53 Correctable Fault Location Register - cache
Side Reserved Type
31
30
29 26 25 24 23 14 13 5 4 2 1 0
Way Index
Reserved
Reserved


















