System Control Coprocessor
ARM DDI 0363E Copyright © 2009 ARM Limited. All rights reserved. 4-15
ID013010 Non-Confidential, Unrestricted Access
The contents of the Main ID Register depend on the specific implementation. Table 4-3 shows
how the bit values correspond with the Main ID Register functions.
Note
If an
MRC
instruction is executed with CRn = c0, Opcode_1 = 0, CRm = c0, and an Opcode_2
value corresponding to an unimplemented or reserved ID register, the system control
coprocessor returns the value of the main ID register.
To access the Main ID Register, read CP15 with:
MRC p15, 0, <Rd>, c0, c0, 0 ; Read Main ID Register
For more information on the processor features, see The Processor Feature Registers on
page 4-18.
4.2.3 c0, Cache Type Register
The Cache Type Register determines the instruction and data minimum line length in bytes to
enable a range of addresses to be invalidated.
The Cache Type Register is:
• a read-only register
• accessible in Privileged mode only.
The contents of the Cache Type Register depend on the specific implementation. Figure 4-8
shows the arrangement of bits in the register.
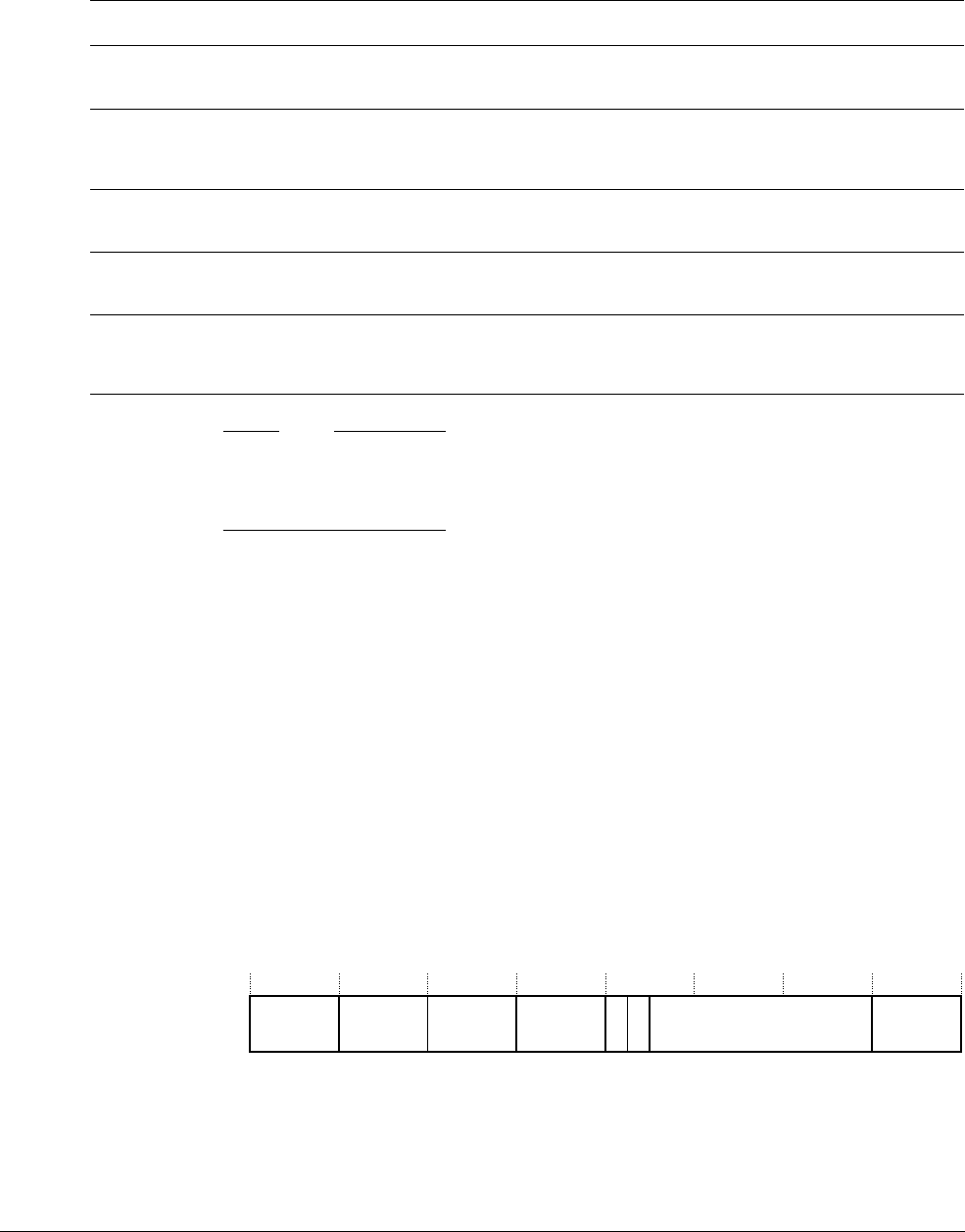
Figure 4-8 Cache Type Register format
Table 4-3 Main ID Register bit functions
Bits Field Function
[31:24] Implementer Indicates implementer.
0x41
- ARM Limited.
[23:20] Variant Identifies the major revision of the processor. This is the major revision number n in
the rn part of the rnpn description of the product revision status. See Product revision
information on page 1-24 for details of the value of this field.
[19:16] Architecture Indicates the architecture version.
0xF
- see feature registers.
[15:4] Primary part number Indicates processor part number.
0xC14
- Cortex-R4.
[3:0] Revision Identifies the minor revision of the processor. This is the minor revision number n in
the pn part of the rnpn description of the product revision status. See Product revision
information on page 1-24 for details of the value of this field.
1CWG ERG IMinLineReserved
31 0
DMinLine 1
3413141516192028 27
Reserved
24 23