5-2
Cisco ONS 15454 Installation and Operations Guide
78-13453-01
Chapter 5 SONET Topologies
Bidirectional Line Switched Rings
Note Two-fiber BLSRs can support up to 24 ONS 15454s, but switch times are slightly longer for rings
containing more than 16 nodes. BLSRs with 16 or fewer nodes will meet the GR-1230 switch time
requirement. Four-fiber BLSRs can only support 16 nodes.
5.2.1 Two-Fiber BLSRs
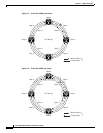
In two-fiber BLSRs, each fiber is divided into working and protect bandwidths. For example, in an
OC-48 BLSR (Figure 5-1), STSs 1 – 24 carry the working traffic, and STSs 25 – 48 are reserved for
protection. Working traffic (STSs 1 – 24) travels in one direction on one fiber and in the opposite
direction on the second fiber. The Cisco Transport Controller (CTC) circuit routing routines calculate
the “shortest path” for circuits based on many factors, including requirements set by the circuit
provisioner, traffic patterns, and distance. For example, in Figure 5-1, circuits going from Node 0 to
Node 1 typically will travel on Fiber 1, unless that fiber is full, in which case circuits will be routed on
Fiber 2 through Node 3 and Node 2. Traffic from Node 0 to Node 2 (or Node 1 to Node 3), may be routed
on either fiber, depending on circuit provisioning requirements and traffic loads.
Figure 5-1 A four-node, two-fiber BLSR
Node 0
Node 1
Node 2
Node 3 OC-48 Ring
= Fiber 1
= Fiber 2
61938
STSs 1-24 (working)
STSs 25-48 (protect)
STSs 1-24 (working)
STSs 25-48 (protect)