64-3
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Configuration Guide using ASDM
Chapter 64 Configuring the ASA CSC Module
Information About the CSC SSM
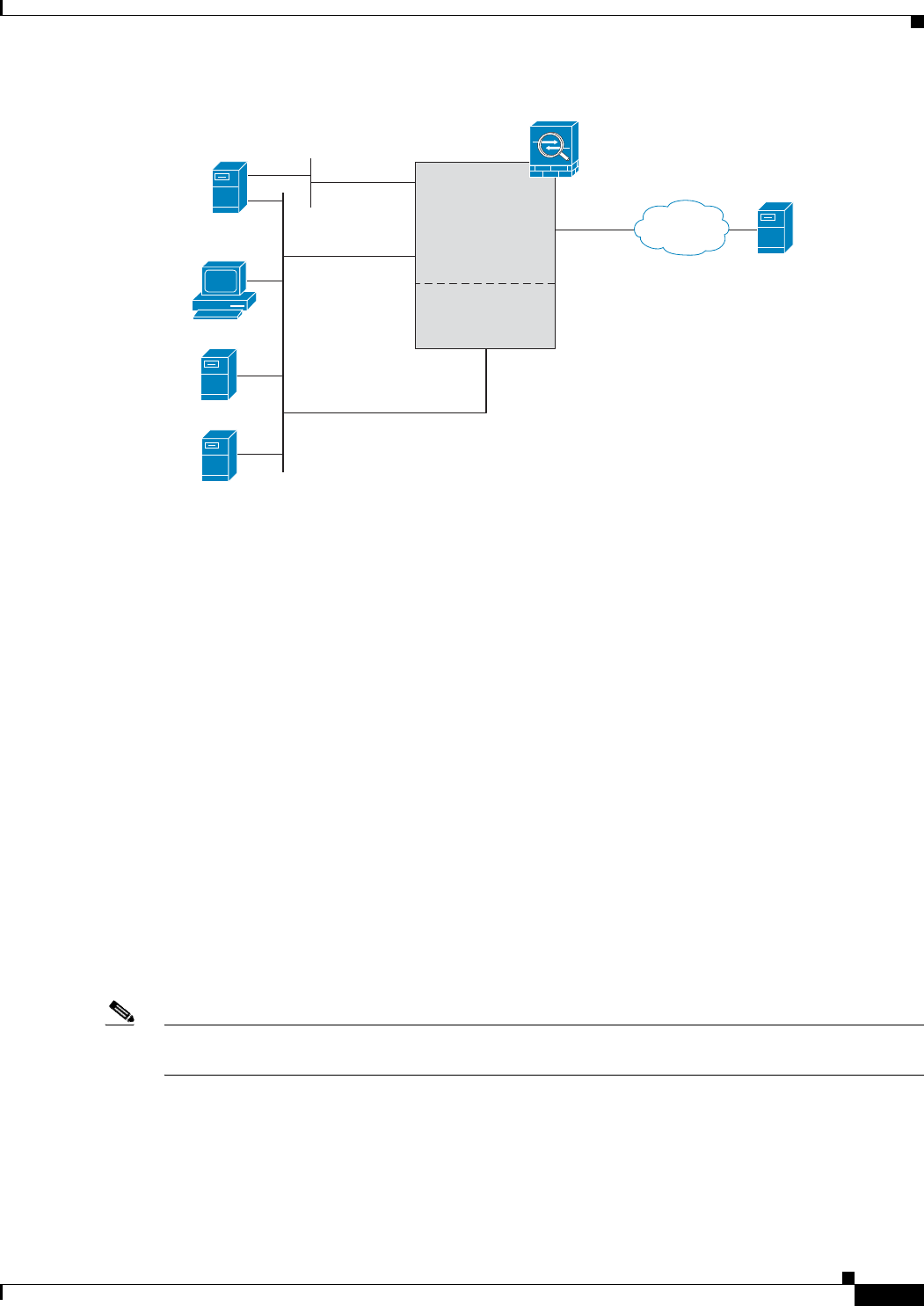
Figure 64-2 CSC SSM Deployment with a Management Network
Determining What Traffic to Scan
The CSC SSM can scan FTP, HTTP/HTTPS, POP3, and SMTP traffic only when the destination port of
the packet requesting the connection is the well-known port for the specified protocol. The CSC SSM
can scan only the following connections:
• FTP connections opened to TCP port 21.
• HTTP connections opened to TCP port 80.
• HTTPS connections opened to TCP port 443.
• POP3 connections opened to TCP port 110.
• SMTP connections opened to TCP port 25.
You can choose to scan traffic for all of these protocols or any combination of them. For example, if you
do not allow network users to receive POP3 e-mail, do not configure the ASA to divert POP3 traffic to
the CSC SSM. Instead, block this traffic.
To maximize performance of the ASA and the CSC SSM, divert only the traffic to the CSC SSM that
you want the CSC SSM to scan. Diverting traffic that you do not want scanned, such as traffic between
a trusted source and destination, can adversely affect network performance.
Note When traffic is first classified for CSC inspection, it is flow-based. If traffic is part of a pre-existing
connection, the traffic goes directly to the service policy set for that connection.
You can apply service policies that include CSC scanning globally or to specific interfaces; therefore,
you can choose to enable CSC scans globally or for specific interfaces. For more information, see the
“Determining Service Policy Rule Actions for CSC Scanning” section on page 64-9.
148387
192.168.100.1
192.168.50.1
Notifications
SMTP Server
192.168.50.38
SSM
management
port
10.6.13.67
Trend Micro
Update Server
ASA
Main System
inside
CSC SSM
outside
HTTP
Proxy
management port
ASDM
Syslog
Internet


















