34-9
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Configuration Guide using ASDM
Chapter 34 Configuring Twice NAT (ASA 8.3 and Later)
Configuring Twice NAT
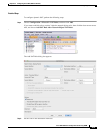
c. For the Match Criteria: Translated Packet > Destination Address, click the browse button and
choose an existing network object, group, or interface or create a new object or group from the
Browse Translated Destination Address dialog box.
For identity NAT for the destination address, simply use the same object or group for both the real
and mapped addresses.
If you want to translate the destination address, then the static mapping is typically one-to-one, so
the real addresses have the same quantity as the mapped addresses. You can, however, have different
quantities if desired. For more information, see the “Static NAT” section on page 32-3. See the
“Guidelines and Limitations” section on page 34-2 for information about disallowed mapped IP
addresses.
For static interface NAT with port translation only, choose an interface from the Browse dialog box.
Be sure to also configure a service translation (see Step 7). For this option, you must configure a
specific interface for the Source Interface in Step 2. See the “Static Interface NAT with Port
Translation” section on page 32-5 for more information.
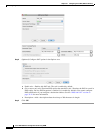
Step 7 (Optional) Identify the translated packet port (the real destination port). For the Match Criteria:
Translated Packet > Service, click the browse button and choose an existing TCP or UDP service
object or create a new object from the Browse Translated Service dialog box.
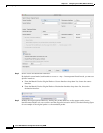
Dynamic NAT does not support port translation. However, because the destination translation is always
static, you can perform port translation for the destination port. A service object can contain both a
source and destination port, but only the destination port is used in this case. If you specify the source
port, it will be ignored. NAT only supports TCP or UDP. When translating a port, be sure the protocols
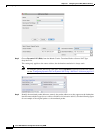
in the real and mapped service objects are identical (both TCP or both UDP). For identity NAT, you can
use the same service object for both the real and mapped ports. The “not equal” (!=) operator is not
supported.