CHAPTER 6 PERIPHERAL HARDWARE FUNCTION
184 User’s Manual U10676EJ3V0UM
6.6 Bit Sequential Buffer ... 16 Bits
The bit sequential buffer (BSB) is a special data memory used for bit manipulation. It can manipulate bits by
sequentially changing the address and bit specification. Therefore, this buffer is useful for processing data with a
long bit length in bit units.
This data memory is configured of 16 bits and can be addressed by a bit manipulation instruction in the pmem.@L
addressing mode. Its bits can be indirectly specified by the L register. The processing can be executed by only
incrementing or decrementing the L register in a program loop and by moving the specified bit sequentially.
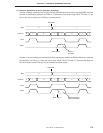
Figure 6-52. Format of Bit Sequential Buffer
3 2 1 0
BSB3
FC3H
L = FH L = CH
3
2 1 0
BSB2
L = BH L = 8H
3
2 1 0
BSB1
L = 7H L = 4H
3
2 1 0
BSB0
L = 3H L = 0H
FC2H FC1H FC0H
INCS L
DECS L
L register
Symbol
Bit
Address
Remarks 1. The specified bit is moved according to the L register in the pmem.@L addressing mode.
2. BSB can be manipulated at any time in the pmem.@L addressing mode, regardless of the
specification of MBE and MBS.
The data in this buffer can also be manipulated even in direct addressing mode. By using 1-, 4-, or 8-bit direct
addressing mode and pmem.@L addressing mode in combination, 1-bit data can be successively input or output.
To manipulate BSB in 8-bit units, the higher and lower 8 bits are manipulated by specifying BSB0 and BSB2.