6-14 User Guide for the Avaya P580 and P882 Multiservice Switches, v6.1
Chapter 6
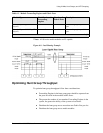
Hunt groups expand the capacity of the core switched backbone. While
there is no specific limit on the number of ports in a hunt group (see “Hunt
Group Configuration Considerations”). In the example, the hunt group
consists of two full-duplex Gigabit Ethernet links shared between two
switches, for an aggregate capacity of 4 Gbps. Enterprise-level servers can
be directly attached to the switching core using either 100 Mbps or Gigabit
Ethernet connections. Fault-tolerant spanning tree links from the core to the
next level of network spread the distribution and capacity to building or
departmental switching centers. Each of these next-level switches may in
turn support tens (or even hundreds) of work group switches and users.
This section contains the following information and procedures:
■ Hunt Group Features
■ Hunt Group Terminology
■ How Hunt Groups Load Share
■ Hunt Group Example
■ Optimizing Hunt Group Throughput
■ Hunt Group Configuration Considerations
■ Hunt Groups and Multicast Traffic
■ Creating Hunt Groups
■ Adding Ports to the Hunt Group
■ Viewing Hunt Group Members
■ Removing Ports from Hunt Groups
Hunt Group Features
Hunt group features include:
■ Shared traffic load.
■ Fault tolerance — If a port in a group fails, the remaining ports in
the group pick up the traffic load.
■ Support for any number of same-speed same media type
connections in a group — The group is not restricted to a single
module in a switch.