Chapter 6 Principles of Operation
6 – 14
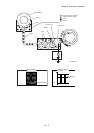
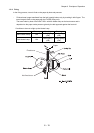
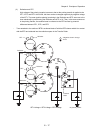
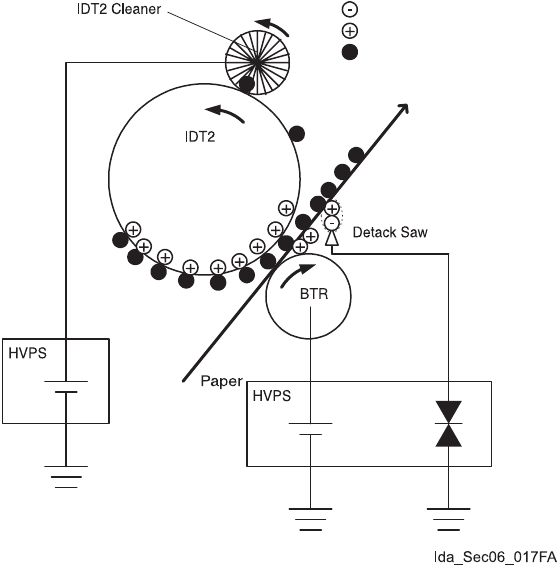
1.3.8 Tertiary transfer (IDT 2 - paper)
In the tertiary transfer process, finished toner image formed on the IDT 2 surface is transferred onto the
paper under the voltage supplied to the BTR (Bias Transfer Roll).
- BTR is composed in the Transfer Roller.
BTR is a conductive roll and receives positive high current from HIGH VOLTAGE POWER
SUPPLY (HVPS).
When paper passes through between IDT2 and BTR, plus potential is given to the back side of the
paper so that the toner on the IDT 2 is transferred onto the paper. At this time, potential on the
BTR is higher than that on the IDT 2.
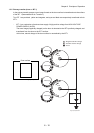
1.3.9 Cleaning (IDT 2)
In the cleaning process, toner remaining on the IDT 2 after the toner image is transferred onto the
paper is temporarily held at the IDT 2 cleaner.
- The IDT 2 cleaner is a conductive roll brush and receives positive high voltage from HIGH
VOLTAGE POWER SUPPLY (HVPS).
The IDT 2 cleaner is placed in contact with the IDT 2 at a position through which it passes after the
toner image having been transferred from IDT 1 is transferred onto the paper. Remaining toner on
the IDT 2 is electrically scraped and held at the IDT 2 cleaner.
The toner held is collected upon completion of printing or at the cleaning cycle. (Refer to "1.3.12
Cleaning (general)".)
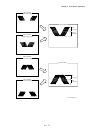
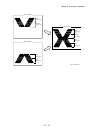
1.3.10 Static elimination
In the static elimination process, negative DC voltage is given to the back side of the paper from the
Detack Saw (static elimination board) to neutralize and eliminate the charge of paper.
- The Detack Saw is held at a constant voltage by the varistor.
The positive charge caused in the tertiary transfer process generates image quality troubles by
scattering toner. Static electricity of the paper is eliminated by discharge of the Detack Saw
preventing those image quality troubles.
: Negative electric charge
: Positive electric charge
: Toner