Symbolic Manipulation 253
Specifying Domain Constraints
Specifying Domain ConstraintsSpecifying Domain Constraints
Specifying Domain Constraints
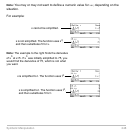
Many identities and transformations are valid for only a particular domain. For example:
Use the
“with” operator to specify the domain constraint.
- Substituting for more general
expressions (either
møc
2
=e
or
c
2
øm=e) may not work as you
anticipate.
Note: Use the solve function to help determine
the single-variable substitution.
ln(x†y) = ln(x) + ln(y) only if x and/or y is
not negative
Sin
-
1
(sin(q)) = q
only if q ‚ Lp
/2 and q
p
/2 radians
Because ln(x†y) = ln(x) + ln(y) is not always valid,
the logarithms are not combined.
With a constraint, the identity is valid and the
expression is simplified.
No match for
substitution