Chapter 3 Signal Connections
© National Instruments Corporation 3-5 Lab-PC+ User Manual
-
+
Instrumentation
Amplifier
+
-
Measured
Voltage
V
m
= [V
in
+ - V
in
-] * GAIN
V
in
-
V
m
V
in
+
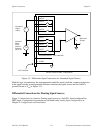
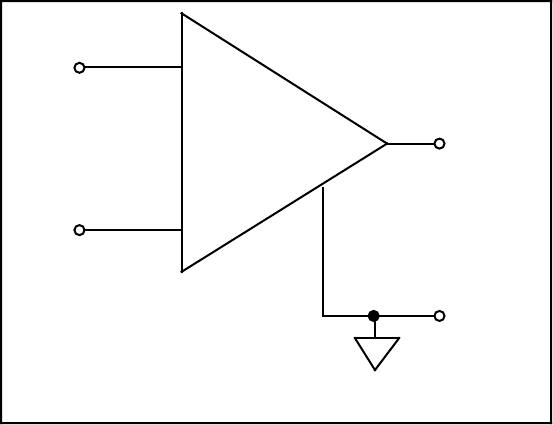
Figure 3-2. Lab-PC+ Instrumentation Amplifier
The Lab-PC+ instrumentation amplifier applies gain, common-mode voltage rejection, and high-
input impedance to the analog input signals connected to the Lab-PC+ board. Signals are routed
to the positive and negative inputs of the instrumentation amplifier through input multiplexers on
the Lab-PC+. The instrumentation amplifier converts two input signals to a signal that is the
difference between the two input signals multiplied by the gain setting of the amplifier. The
amplifier output voltage is referenced to the Lab-PC+ ground. The Lab-PC+ ADC measures this
output voltage when it performs A/D conversions.
All signals must be referenced to ground, either at the source device or at the Lab-PC+. If you
have a floating source, you must use a ground-referenced input connection at the Lab-PC+. If
you have a grounded source, you must use a non-referenced input connection at the Lab-PC+.
Types of Signal Sources
When configuring the input mode of the Lab-PC+ and making signal connections, you should
first determine whether the signal source is floating or ground-referenced. These two types of
signals are described as follows.
Floating Signal Sources
A floating signal source is one that is not connected in any way to the building ground system
but rather has an isolated ground reference point. Some examples of floating signal sources are
outputs of transformers, thermocouples, battery-powered devices, optical isolator outputs, and
isolation amplifiers. The ground reference of a floating signal must be tied to the Lab-PC+
analog input ground in order to establish a local or onboard reference for the signal. Otherwise,