Chapter 13 Interfaces
ZyWALL USG 300 User’s Guide
335
13.8 VLAN Interfaces
A Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN) divides a physical network into multiple
logical networks. The standard is defined in IEEE 802.1q.
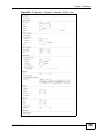
Figure 281 Example: Before VLAN
In this example, there are two physical networks and three departments A, B, and
C. The physical networks are connected to hubs, and the hubs are connected to
the router.
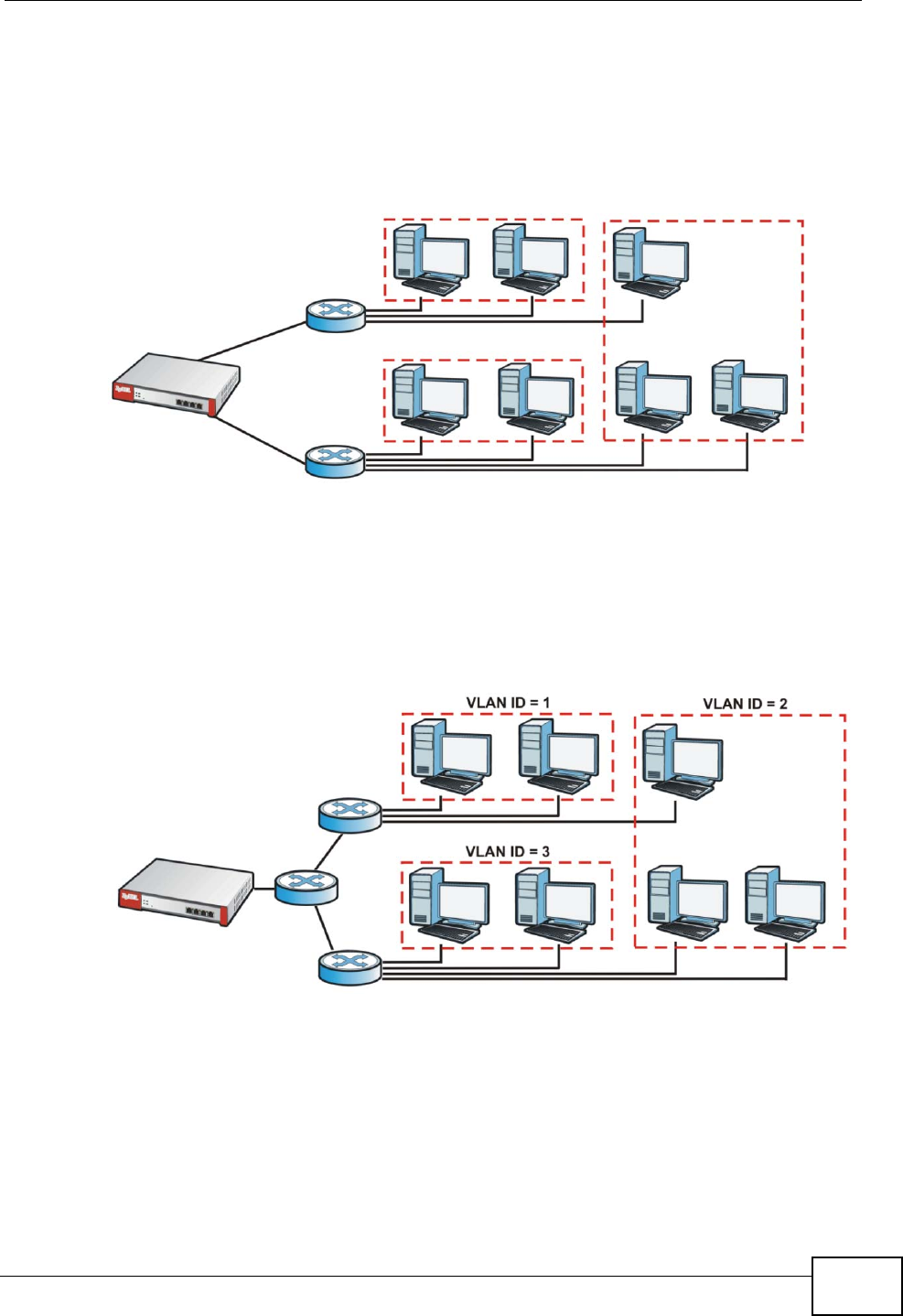
Alternatively, you can divide the physical networks into three VLANs.
Figure 282 Example: After VLAN
Each VLAN is a separate network with separate IP addresses, subnet masks, and
gateways. Each VLAN also has a unique identification number (ID). The ID is a 12-
bit value that is stored in the MAC header. The VLANs are connected to switches,
and the switches are connected to the router. (If one switch has enough
connections for the entire network, the network does not need switches A and B.)
A
B
C
A
B