Chapter 14 Trunks
ZyWALL USG 300 User’s Guide
366
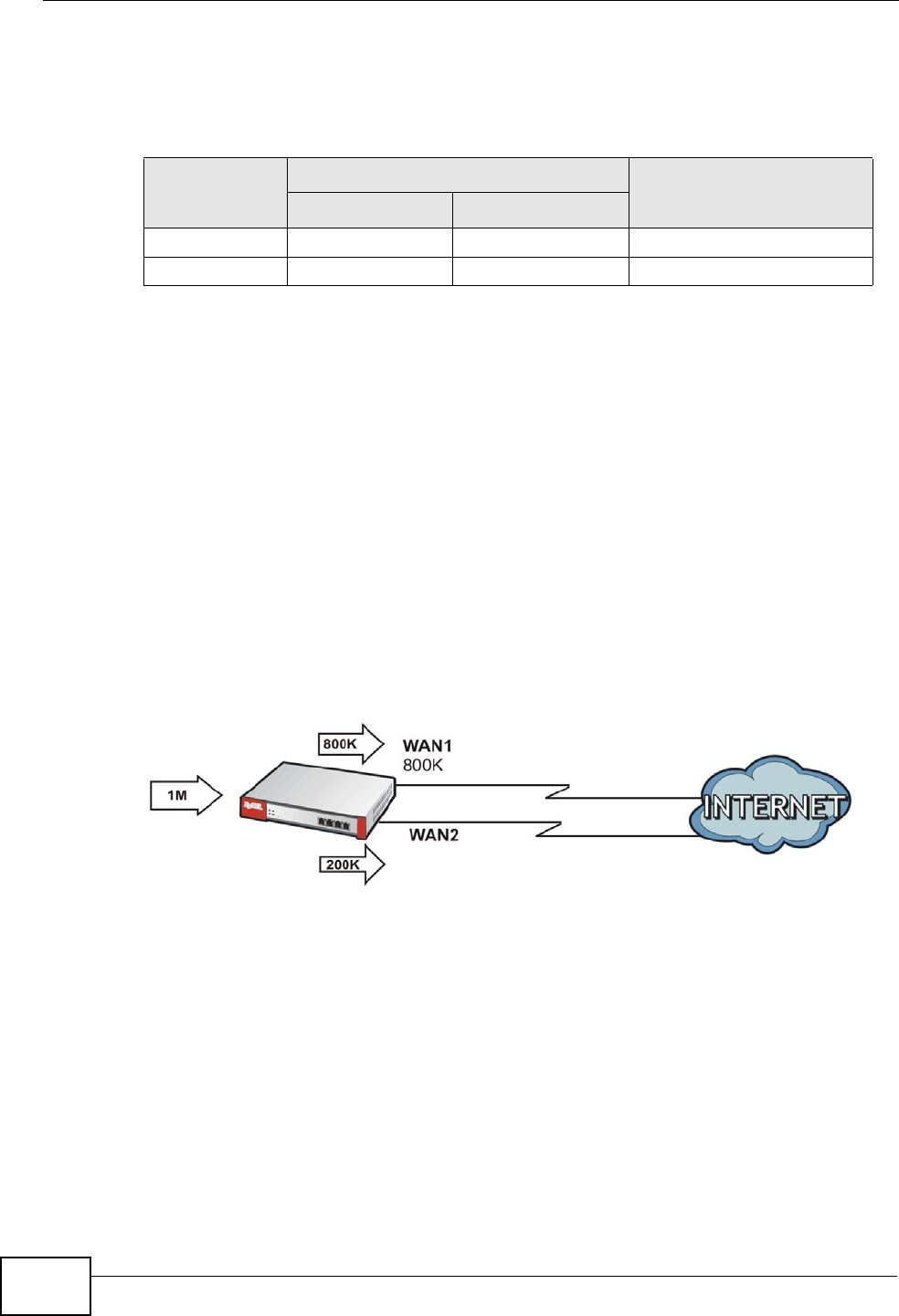
Since WAN 2 has a smaller load balancing index (meaning that it is less utilized
than WAN 1), the ZyWALL will send the subsequent new session traffic through
WAN 2.
Weighted Round Robin
The Weighted Round Robin (WRR) algorithm is best suited for situations when the
bandwidths set for the two WAN interfaces are different. Similar to the Round
Robin (RR) algorithm (see Section 14.4 on page 371), the Weighted Round Robin
(WRR) algorithm sets the ZyWALL to send traffic through each WAN interface in
turn. In addition, the WAN interfaces are assigned weights. An interface with a
larger weight gets more of the traffic than an interface with a smaller weight.
For example, in the figure below, the configured available bandwidth of ge2 is 1M
and ge3 is 512K. You can set the ZyWALL to distribute the network traffic between
the two interfaces by setting the weight of ge2 and ge3 to 2 and 1 respectively.
The ZyWALL assigns the traffic of two sessions to ge2 for every session's traffic
assigned to ge3.
Figure 292 Weighted Round Robin Algorithm Example
Spillover
The spillover load balancing algorithm sends network traffic to the first interface in
the trunk member list until the interface’s maximum allowable load is reached,
then sends the excess network traffic of new sessions to the next interface in the
trunk member list. This continues as long as there are more member interfaces
and traffic to be sent through them.
Suppose the first trunk member interface uses an unlimited access Internet
connection and the second is billed by usage. Spillover load balancing only uses
the second interface when the traffic load exceeds the threshold on the first
Table 86 Least Load First Example
INTERFACE
OUTBOUND
LOAD BALANCING INDEX
(M/A)
AVAILABLE (A) MEASURED (M)
WAN 1 512 K 412 K 0.8
WAN 2 256 K 198 K 0.77