Chapter 16 Routing Protocols
ZyWALL USG 300 User’s Guide
391
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
16.3 The OSPF Screen
OSPF (Open Shortest Path First, RFC 2328) is a link-state protocol designed to
distribute routing information within a group of networks, called an Autonomous
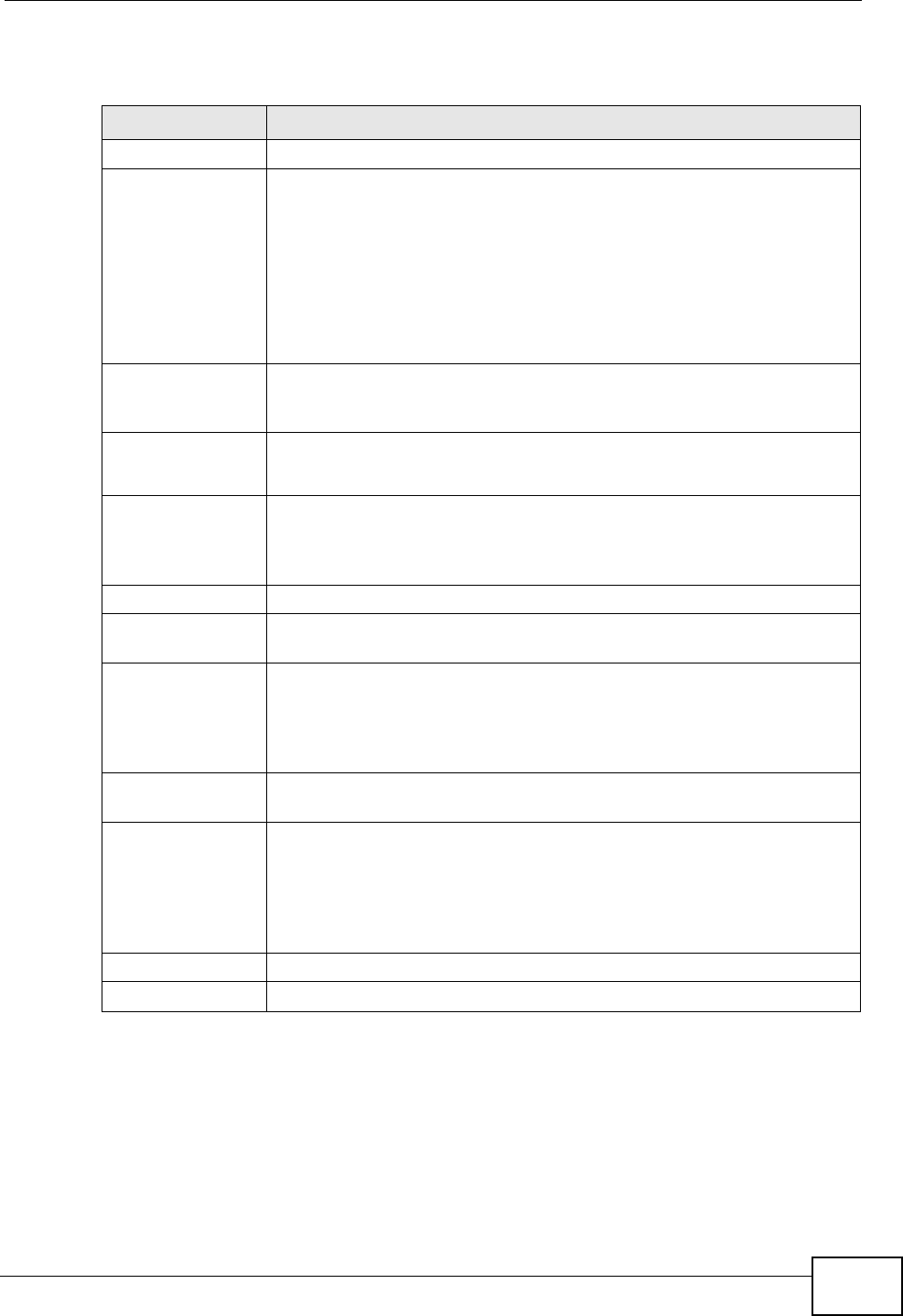
Table 95 Configuration > Network > Routing Protocol > RIP
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Authentication
Authentication Select the authentication method used in the RIP network. This
authentication protects the integrity, but not the confidentiality, of
routing updates.
None uses no authentication.
Text uses a plain text password that is sent over the network (not
very secure).
MD5 uses an MD5 password and authentication ID (most secure).
Text
Authentication
Key
This field is available if the Authentication is Text. Type the
password for text authentication. The key can consist of alphanumeric
characters and the underscore, and it can be up to 8 characters long.
MD5
Authentication
ID
This field is available if the Authentication is MD5. Type the ID for
MD5 authentication. The ID can be between 1 and 255.
MD5
Authentication
Key
This field is available if the Authentication is MD5. Type the
password for MD5 authentication. The password can consist of
alphanumeric characters and the underscore, and it can be up to 16
characters long.
Redistribute
Active OSPF Select this to use RIP to advertise routes that were learned through
OSPF.
Metric Type the cost for routes provided by OSPF. The metric represents the
“cost” of transmission for routing purposes. RIP routing uses hop
count as the measurement of cost, with 1 usually used for directly
connected networks. The number does not have to be precise, but it
must be between 0 and 16. In practice, 2 or 3 is usually used.
Active Static
Route
Select this to use RIP to advertise routes that were learned through
the static route configuration.
Metric Type the cost for routes provided by the static route configuration.
The metric represents the “cost” of transmission for routing purposes.
RIP routing uses hop count as the measurement of cost, with 1
usually used for directly connected networks. The number does not
have to be precise, but it must be between 0 and 16. In practice, 2 or
3 is usually used.
Apply Click this button to save your changes to the ZyWALL.
Reset Click this button to return the screen to its last-saved settings.


















