Chapter 35 ADP
ZyWALL USG 300 User’s Guide
639
UDP Flood Attack
UDP is a connection-less protocol and it does not require any connection setup
procedure to transfer data. A UDP flood attack is possible when an attacker sends
a UDP packet to a random port on the victim system. When the victim system
receives a UDP packet, it will determine what application is waiting on the
destination port. When it realizes that there is no application that is waiting on the
port, it will generate an ICMP packet of destination unreachable to the forged
source address. If enough UDP packets are delivered to ports on victim, the
system will go down.
Protocol Anomaly Background Information
The following sections may help you configure the protocol anomaly profile screen
(see Section 35.3.5 on page 631)
HTTP Inspection and TCP/UDP/ICMP Decoders
The following table gives some information on the HTTP inspection, TCP decoder,
UDP decoder and ICMP decoder ZyWALL protocol anomaly rules.
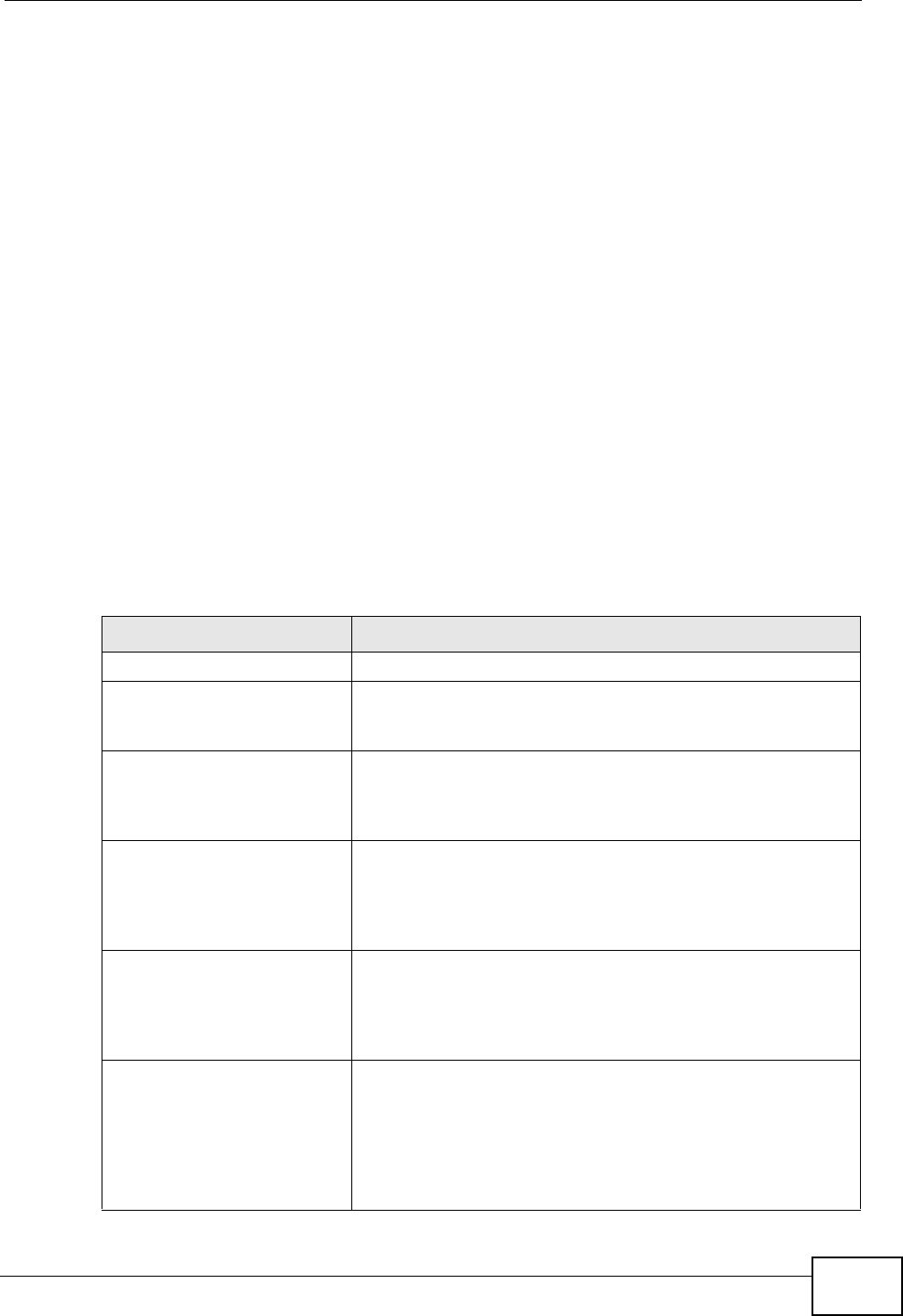
Table 174 HTTP Inspection and TCP/UDP/ICMP Decoders
LABEL DESCRIPTION
HTTP Inspection
APACHE-WHITESPACE
ATTACK
This rule deals with non-RFC standard of tab for a space
delimiter. Apache uses this, so if you have an Apache
server, you need to enable this option.
ASCII-ENCODING
ATTACK
This rule can detect attacks where malicious attackers use
ASCII-encoding to encode attack strings. Attackers may
use this method to bypass system parameter checks in
order to get information or privileges from a web server.
BARE-BYTE-
UNICODING-ENCODING
ATTACK
Bare byte encoding uses non-ASCII characters as valid
values in decoding UTF-8 values. This is NOT in the HTTP
standard, as all non-ASCII values have to be encoded with
a %. Bare byte encoding allows the user to emulate an IIS
server and interpret non-standard encodings correctly.
BASE36-ENCODING
ATTACK
This is a rule to decode base36-encoded characters. This
rule can detect attacks where malicious attackers use
base36-encoding to encode attack strings. Attackers may
use this method to bypass system parameter checks in
order to get information or privileges from a web server.
DIRECTORY-TRAVERSAL
ATTACK
This rule normalizes directory traversals and self-referential
directories. So, “/abc/this_is_not_a_real_dir/../xyz” get
normalized to “/abc/xyz”. Also, “/abc/./xyz” gets
normalized to “/abc/xyz”. If a user wants to configure an
alert, then specify “yes”, otherwise “no”. This alert may give
false positives since some web sites refer to files using
directory traversals.